Higher order arrangement of the eukaryotic nuclear bodies
- PMID: 12361981
- PMCID: PMC129717
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.212483099
Higher order arrangement of the eukaryotic nuclear bodies
Abstract
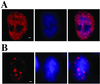
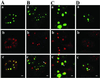
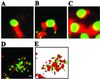
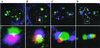
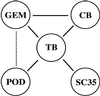
The nuclei of eukaryotic cells consist of discrete substructures. These substructures include the nuclear bodies, which have been implicated in a number of biological processes such as transcription and splicing. However, for most nuclear bodies, the details of involvement in these processes in relation to their three-dimensional distributions in the nucleus are still unclear. Through the analysis of TDP, a protein functional in both transcriptional repression and alternative splicing, we have identified a new category of nuclear bodies within which the TDP molecules reside. Remarkably, the TDP bodies (TBs) colocalize or overlap with several different types of nuclear bodies previously suggested to function in transcription or splicing. Of these nuclear bodies, the Gemini of coiled bodies (GEM) seems to associate with TB through the interaction between survival motor neuron (SMN) protein and TDP. Furthermore, TB sometimes appears to be the bridge of two or more of these other nuclear bodies. Our data suggest the existence of a hierarchy and possibly functional arrangement of the nuclear bodies within the eukaryotic nuclei.
Figures

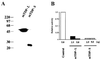

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

