Synonymous codon usage is subject to selection in thermophilic bacteria
- PMID: 12364606
- PMCID: PMC140546
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf546
Synonymous codon usage is subject to selection in thermophilic bacteria
Abstract
The patterns of synonymous codon usage, both within and among genomes, have been extensively studied over the past two decades. Despite the accumulating evidence that natural selection can shape codon usage, it has not been possible to link a particular pattern of codon usage to a specific external selective force. Here, we have analyzed the patterns of synonymous codon usage in 40 completely sequenced prokaryotic genomes. By combining the genes from several genomes (more than 80 000 genes in all) into a single dataset for this analysis, we were able to investigate variations in codon usage, both within and between genomes. The results show that synonymous codon usage is affected by two major factors: (i) the overall G+C content of the genome and (ii) growth at high temperature. This study focused on the relationship between synonymous codon usage and the ability to grow at high temperature. We have been able to eliminate both phylogenetic history and lateral gene transfer as possible explanations for the characteristic pattern of codon usage among the thermophiles. Thus, these results demonstrate a clear link between a particular pattern of codon usage and an external selective force.
Figures
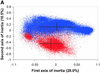




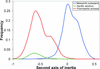
References
-
- Ikemura T. (1981) Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J. Mol. Biol., 146, 1. - PubMed
-
- Ikemura T. (1981) Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J. Mol. Biol., 151, 389–409. - PubMed
-
- Ikemura T. (1982) Differences in synonymous codon choice patterns of yeast and correlation between the abundance of yeast transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in protein genes. Differences in synonymous codon choice patterns of yeast. J. Mol. Biol., 158, 573–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

