Lipopolysaccharide induces overexpression of MUC2 and MUC5AC in cultured biliary epithelial cells: possible key phenomenon of hepatolithiasis
- PMID: 12368220
- PMCID: PMC1867307
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64423-9
Lipopolysaccharide induces overexpression of MUC2 and MUC5AC in cultured biliary epithelial cells: possible key phenomenon of hepatolithiasis
Abstract
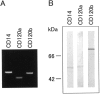
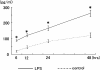
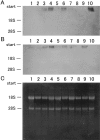
Bacterial infection, bile stasis, mucin hypersecretion, and an alteration of the mucin profile such as an aberrant expression of gel-forming apomucin (MUC2 and MUC5AC) in the intrahepatic biliary tree are thought to be important in the lithogenesis of hepatolithiasis. So far, there have been no detailed studies linking bacterial infection to altered mucus secretion of biliary epithelium. In this study, the influence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a bacterial component, on apomucin expression in cultured murine biliary epithelial cells was examined with emphasis on the participation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha. It was found that LPS up-regulated the expression of MUC2 and MUC5AC in cultured murine biliary epithelial cells. LPS also induced the expression of TNF-alpha in biliary epithelial cells and its secretion into the culture medium. The up-regulation of these apomucins was inhibited by pretreatment with TNF-alpha antibody. TNF-alpha alone also induced the overexpression of MUC2 and MUC5AC in cultured biliary epithelial cells. This overexpression was inhibited by pretreatment with calphostin C, an inhibitor of protein kinase C. These findings suggest that LPS can induce overexpression of MUC2 and MUC5AC in biliary epithelial cells via synthesis of TNF-alpha and activation of protein kinase C. This mechanism might be involved in the lithogenesis of hepatolithiasis.
Figures
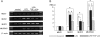



Similar articles
-
PGE(2) induces MUC2 and MUC5AC expression in human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells via EP4/p38MAPK activation.Ann Hepatol. 2013 May-Jun;12(3):479-86. Ann Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23619266
-
Lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli stimulates mucin secretion by cultured dog gallbladder epithelial cells.Hepatology. 1999 May;29(5):1352-7. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290515. Hepatology. 1999. PMID: 10216115
-
Expression of apomucins in the intrahepatic biliary tree in hepatolithiasis differs from that in normal liver and extrahepatic biliary obstruction.Hepatology. 1998 Jan;27(1):54-61. doi: 10.1002/hep.510270110. Hepatology. 1998. PMID: 9425917
-
Differential Muc2 and Muc5ac secretion by stimulated guinea pig tracheal epithelial cells in vitro.Respir Res. 2006 Feb 25;7(1):35. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-35. Respir Res. 2006. PMID: 16504136 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and culture of biliary epithelial cells.Gut. 1994 Jul;35(7):875-8. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.7.875. Gut. 1994. PMID: 8063212 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small duct autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis and Crohn colitis in a 10-year-old child. A case report and review of the literature.Diagn Pathol. 2012 Aug 14;7:100. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-100. Diagn Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22891962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of p38 mitogen-activate protein kinase on MUC5AC protein expression of bile duct epithelial cells in hepatolithiasis patients.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Oct 1;8(10):13753-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26722604 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Hormones and Vaginal Microflora on the Glycome of the Female Genital Tract: Cervical-Vaginal Fluid.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 20;11(7):e0158687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158687. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27437931 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented expression of hepatocytes growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 (HAI-1) in intrahepatic small bile ducts in primary biliary cirrhosis.Virchows Arch. 2006 Oct;449(4):462-71. doi: 10.1007/s00428-006-0257-7. Epub 2006 Aug 29. Virchows Arch. 2006. PMID: 16941151
-
MUC1: a multifunctional cell surface component of reproductive tissue epithelia.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2004 Jan 7;2:4. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-2-4. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 14711375 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sasaki M, Nakanuma Y, Kim YS: Expression of apomucins in the intrahepatic biliary tree in hepatolithiasis differ from that in normal liver and extrahepatic biliary obstruction. Hepatology 1998, 27:46-53 - PubMed
-
- Nakanuma Y, Yamaguchi K, Ohta G, Terada T: Pathologic features of hepatolithiasis in Japan. Hum Pathol 1988, 19:1181-1186 - PubMed
-
- Neutra MR, Foretner JF: Gastrointestinal mucus: synthesis, secretion and function. Johnson LR eds. Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. 1987:pp 975-1009 Raven Press, New York
-
- Kim YS, Gum JR: Diversity of mucin genes, structure, function, and expression. Gastroenterology 1995, 109:999-1013 - PubMed
-
- Bobek LA, Tsai H, Biesbrock AR, Levine MJ: Molecular cloning, sequence, and specificity of expression of the gene encoding the low molecular weight human salivary mucin (MUC7). J Biol Chem 1993, 268:20563-20569 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

