Draft sequencing and comparative genomics of Xylella fastidiosa strains reveal novel biological insights
- PMID: 12368248
- PMCID: PMC187531
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.370702
Draft sequencing and comparative genomics of Xylella fastidiosa strains reveal novel biological insights
Abstract
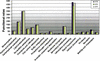
Draft sequencing is a rapid and efficient method for determining the near-complete sequence of microbial genomes. Here we report a comparative analysis of one complete and two draft genome sequences of the phytopathogenic bacterium, Xylella fastidiosa, which causes serious disease in plants, including citrus, almond, and oleander. We present highlights of an in silico analysis based on a comparison of reconstructions of core biological subsystems. Cellular pathway reconstructions have been used to identify a small number of genes, which are likely to reside within the draft genomes but are not captured in the draft assembly. These represented only a small fraction of all genes and were predominantly large and small ribosomal subunit protein components. By using this approach, some of the inherent limitations of draft sequence can be significantly reduced. Despite the incomplete nature of the draft genomes, it is possible to identify several phage-related genes, which appear to be absent from the draft genomes and not the result of insufficient sequence sampling. This region may therefore identify potential host-specific functions. Based on this first functional reconstruction of a phytopathogenic microbe, we spotlight an unusual respiration machinery as a potential target for biological control. We also predicted and developed a new defined growth medium for Xylella.
Figures

References
-
- Davis MJ, Thompson SV. Etiological role of a xylem-limited bacterium causing Pierce's disease in almond leaf scorch. Phytopathology. 1980;70:472–475.
-
- Davis MJ, Purcell AH, Thompson SV. Pierce's disease of grapevines: Isolation of the causal bacterium. Science. 1978;199:75–77. - PubMed
-
- Davis MJ, Whitcomb RF, Gillespie AG., Jr . Fastidious bacteria of plant vascular tissue and invertebrates (including so called rickettsia-like bacteria) In: Starr MP, Stolp H, Truper HG, Balows A, Schlegel HG, editors. The prokaryotes: A handbook on habits, isolation, and identification of bacteria. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 1981a. pp. 2172–2188.
-
- Davis MJ, French WJ, Schaad NW. Axenic culture of the bacteria associated with phony disease of peach and plum leaf scald. Curr Microbiol. 1981b;6:309–314.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
