Critical points in charged membranes containing cholesterol
- PMID: 12368466
- PMCID: PMC129683
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.212522699
Critical points in charged membranes containing cholesterol
Abstract
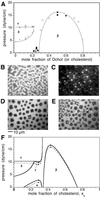
Epifluorescence microscopy is used to determine phase diagrams for lipid monolayers containing binary mixtures of cholesterol or dihydrocholesterol and dimyristoylphosphatidylserine, as well as ternary mixtures that also contain ganglioside G(M1). The phase diagrams are unusual in that they show multiple critical points: two upper miscibility critical points and one lower miscibility critical point. These critical points all are associated with the formation of condensed complexes between these lipids and cholesterol (or dihydrocholesterol). The miscibility critical pressures depend on subphase pH and ionic strength. Changes in critical pressures due to changes in subphase composition are closely related to changes in membrane electrostatic pressure and surface ionization.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Condensed complexes of cholesterol and phospholipids.Biophys J. 1999 Sep;77(3):1507-17. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)76998-5. Biophys J. 1999. PMID: 10465761 Free PMC article.
-
Condensed complexes, rafts, and the chemical activity of cholesterol in membranes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Nov 7;97(23):12422-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.220418097. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11050164 Free PMC article.
-
Miscibility critical pressures in monolayers of ternary lipid mixtures.Biophys J. 2000 Oct;79(4):2033-42. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76451-4. Biophys J. 2000. PMID: 11023907 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral order in binary lipid alloys and its coupling to membrane functions.Chem Phys Lipids. 1991 Mar;57(2-3):363-74. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(91)90086-q. Chem Phys Lipids. 1991. PMID: 2054912 Review.
-
From small fluctuations to large-scale phase separation: lateral organization in model membranes containing cholesterol.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007 Oct;18(5):573-82. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2007.08.016. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17942350 Review.
Cited by
-
Spontaneous formation of two-dimensional and three-dimensional cholesterol crystals in single hydrated lipid bilayers.Biophys J. 2012 Jul 18;103(2):255-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.05.025. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22853903 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast inversion in the epifluorescence of cholesterol-phospholipid monolayers.Biophys J. 2004 Feb;86(2):880-90. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74163-6. Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 14747323 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol homeostasis and the escape tendency (activity) of plasma membrane cholesterol.Prog Lipid Res. 2008 Sep;47(5):319-32. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2008.03.001. Epub 2008 Mar 29. Prog Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18423408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase behavior of lipid monolayers containing DPPC and cholesterol analogs.Biophys J. 2006 May 1;90(9):3176-83. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.072959. Epub 2006 Feb 3. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16461392 Free PMC article.
-
Using monomolecular films to characterize lipid lateral interactions.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;398:41-58. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-513-8_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 18214373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Subramaniam S. & McConnell, H. M. (1987) J. Phys. Chem. 91, 1715-1718.
-
- McConnell H. M. (1991) Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 42, 171-195.
-
- MacDonald R. C., Simon, S. A. & Baer, E. (1976) Biochemistry 15, 885-891. - PubMed
-
- Radhakrishnan A. & McConnell, H. M. (2002) J. Phys. Chem. 106, 4755-4762.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

