A tumor suppressor homolog, AtPTEN1, is essential for pollen development in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 12368500
- PMCID: PMC151231
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.005702
A tumor suppressor homolog, AtPTEN1, is essential for pollen development in Arabidopsis
Abstract
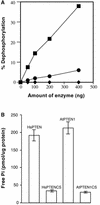
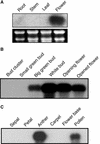
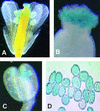
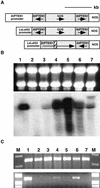
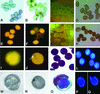
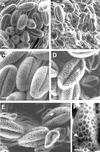
Although it is well known that Tyr phosphatases play a critical role in signal transduction in animal cells, little is understood of the functional significance of Tyr phosphatases in higher plants. Here, we describe the functional analysis of an Arabidopsis gene (AtPTEN1) that encodes a Tyr phosphatase closely related to PTEN, a tumor suppressor in animals. The recombinant AtPTEN1 protein, like its homologs in animals, is an active phosphatase that dephosphorylates phosphotyrosine and phosphatidylinositol substrates. RNA gel blot analysis and examination of promoter-reporter constructs in transgenic Arabidopsis plants revealed that the AtPTEN1 gene is expressed exclusively in pollen grains during the late stage of development. Suppression of AtPTEN1 gene expression by RNA interference caused pollen cell death after mitosis. We conclude that AtPTEN1 is a pollen-specific phosphatase and is essential for pollen development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PHOSPHATIDYLSERINE SYNTHASE1 is required for microspore development in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2011 Aug;67(4):648-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04624.x. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21554450
-
Functional characterization and expression analyses of the glucose-specific AtSTP9 monosaccharide transporter in pollen of Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2003 Sep;133(1):182-90. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.026674. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12970485 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis AtVPS15 is essential for pollen development and germination through modulating phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate formation.Plant Mol Biol. 2011 Oct;77(3):251-60. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9806-9. Epub 2011 Jul 16. Plant Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21833541 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis VAC14 Is Critical for Pollen Development through Mediating Vacuolar Organization.Plant Physiol. 2018 Aug;177(4):1529-1538. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00495. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29884680 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism and roles of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate in pollen development and pollen tube growth in Arabidopsis.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Feb;7(2):165-9. doi: 10.4161/psb.18743. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22307045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Importance of Tyrosine Phosphorylation in Hormone-Regulated Plant Growth and Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 13;23(12):6603. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126603. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formins: emerging players in the dynamic plant cell cortex.Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:712605. doi: 10.6064/2012/712605. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 24278734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Protein Phosphatases and Protein Kinases of Arabidopsis thaliana.Arabidopsis Book. 2007;5:e0106. doi: 10.1199/tab.0106. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Arabidopsis Book. 2007. PMID: 22303230 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of a cytoplasmic male sterility line and associated maintainer line in soybean.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 2;14:1098125. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1098125. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36818857 Free PMC article.
-
Roots of angiosperm formins: the evolutionary history of plant FH2 domain-containing proteins.BMC Evol Biol. 2008 Apr 22;8:115. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-115. BMC Evol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18430232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonhomme, S., Horlow, C., Vezon, D., De Laissardiere, S., Guyon, A., Ferault, M., Marchand, M., Bechtold, N., and Pelletier, G. (1998). T-DNA mediated disruption of essential gametophytic genes in Arabidopsis is unexpectedly rare and cannot be inferred from segregation distortion alone. Mol. Gen. Genet. 260, 444–452. - PubMed
-
- Bozzola, J.J., and Russell, L.D. (1999). Electron Microscopy: Principles and Techniques for Biologists. (Sudbury, MA: John and Bartlett), pp. 50–71.
-
- Clough, S.J., and Bent, A.F. (1998). Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 16, 735–743. - PubMed
-
- Fordham-Skelton, A.R., Skipsey, M., Eveans, I.M., Edwards, R., and Gatehouse, J.A. (1999). Higher plant tyrosine-specific protein phosphatases (PTPs) contain novel amino-terminal domains: Expression during embryogenesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 39, 593–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

