Regulation of the subcellular localization of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)2 by TRAF1 reveals mechanisms of TRAF2 signaling
- PMID: 12370254
- PMCID: PMC2194023
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20020774
Regulation of the subcellular localization of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)2 by TRAF1 reveals mechanisms of TRAF2 signaling
Abstract
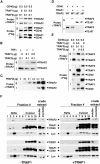
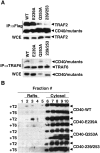
Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)2 is a critical adaptor molecule for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors in inflammatory and immune signaling. Upon receptor engagement, TRAF2 is recruited to CD40 and translocates to lipid rafts in a RING finger-dependent process, which enables the activation of downstream signaling cascades including c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB. Although TRAF1 can displace TRAF2 and CD40 from raft fractions, it promotes the ability of TRAF2 activate signaling over a sustained period of time. Removal of the RING finger of TRAF2 prevents its translocation into detergent-insoluble complexes and renders it dominant negative for signaling. TRAF1(-/-) dendritic cells show attenuated responses to secondary stimulation by TRAF2-dependent factors and increased stimulus-dependent TRAF2 degradation. Replacement of the RING finger of TRAF2 with a raft-targeting signal restores JNK activation and association with the cyto-skeletal protein Filamin, but not NF-kappaB activation. These findings offer insights into the mechanism of TRAF2 signaling and identify a physiological role for TRAF1 as a regulator of the subcellular localization of TRAF2.
Figures





References
-
- Locksley, R.M., N. Killeen, and M.J. Lenardo. 2001. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell. 104:487–501. - PubMed
-
- Wajant, H., F. Henkler, and P. Scheurich. 2001. The TNF-receptor-associated factor family: scaffold molecules for cytokine receptors, kinases and their regulators. Cell. Signal. 13:389–400. - PubMed
-
- Rothe, M., S.C. Wong, W.J. Henzel, and D.V. Goeddel. 1994. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 78:681–692. - PubMed
-
- Park, Y.C., V. Burkitt, A.R. Villa, L. Tong, and H. Wu. 1999. Structural basis for self-association and receptor recognition of human TRAF2. Nature. 398:533–538. - PubMed
-
- Ye, H., Y.C. Park, M. Kreishman, E. Kieff, and H. Wu. 1999. The structural basis for the recognition of diverse receptor sequences by TRAF2. Mol. Cell. 4:321–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

