Interleukin 15 controls both proliferation and survival of a subset of memory-phenotype CD8(+) T cells
- PMID: 12370255
- PMCID: PMC2194030
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20020772
Interleukin 15 controls both proliferation and survival of a subset of memory-phenotype CD8(+) T cells
Abstract
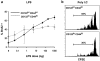
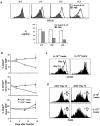
Previous work has shown that memory-phenotype CD44(hi) CD8(+) cells are controlled by a cytokine, interleukin (IL)-15. However, the dependency of CD44(hi) CD8(+) cells on IL-15 is partial rather than complete. Here, evidence is presented that CD44(hi) CD8(+) cells comprise a mixed population of IL-15-dependent and IL-15-independent cells. The major subset of CD122(hi) CD44(hi) CD8(+) cells is heavily dependent on IL-15 by three different parameters, namely (1) "bystander" proliferation induced via IFN-induced stimulation of the innate immune system, (2) normal "background" proliferation, and (3) T cell survival; IL-15 dependency is most extreme for the Ly49(+) subset of CD122(hi) CD44(hi) CD8(+) cells. In contrast to CD122(hi) cells, the CD122(lo) subset of CD44(hi) CD8(+) cells is IL-15 independent; likewise, being CD122(lo), CD44(hi) CD4(+) cells are IL-15 independent. Thus, subsets of memory-phenotype T cells differ radically in their sensitivity to IL-15.
Figures




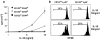
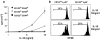


References
-
- Sprent, J., and C.D. Surh. 2001. Generation and maintenance of memory T cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Schluns, K.S., W.C. Kieper, S.C. Jameson, and L. Lefrancois. 2000. Interleukin-7 mediates the homeostasis of naive and memory CD8 T cells in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 1:426–432. - PubMed
-
- Dutton, R.W., L.M. Bradley, and S.L. Swain. 1998. T cell memory. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16:201–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

