A point mutation of Tyr-759 in interleukin 6 family cytokine receptor subunit gp130 causes autoimmune arthritis
- PMID: 12370259
- PMCID: PMC2194024
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20020619
A point mutation of Tyr-759 in interleukin 6 family cytokine receptor subunit gp130 causes autoimmune arthritis
Abstract
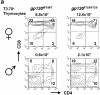
We generated a mouse line in which the src homology 2 domain-bearing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP)-2 binding site of gp130, tyrosine 759, was mutated to phenylalanine (gp130(F759/F759)). The gp130(F759/F759) mice developed rheumatoid arthritis (RA)-like joint disease. The disease was accompanied by autoantibody production and accumulated memory/activated T cells and myeloid cells. Before the disease onset, the T cells were hyperresponsive and thymic selection and peripheral clonal deletion were impaired. The inhibitory effect of IL-6 on Fas ligand expression during activation-induced cell death (AICD) was augmented in gp130(F759/F759) T cells in a manner dependent on the tyrosine residues of gp130 required for signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation. Finally, we showed that disease development was dependent on lymphocytes. These results provide evidence that a point mutation of a cytokine receptor has the potential to induce autoimmune disease.
Figures
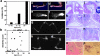
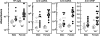
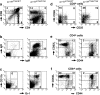
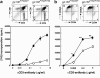


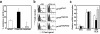
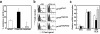
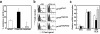
References
-
- Feldmann, M., F.M. Brennan, and R.N. Maini. 1996. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 85:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Hirano, T. 2002. Revival of the autoantibody model in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Immunol. 3:342–344. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann, M., F.M. Brennan, and R.N. Maini. 1996. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:397–440. - PubMed
-
- Hirano, T. 1998. Interleukin 6 and its receptor: ten years later. Int. Rev. Immunol. 16:249–284. - PubMed
-
- O'Shea, J.J., A. Ma, and P. Lipsky. 2002. Cytokines and autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2:37–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

