Regulation and mechanisms of macrophage cholesterol efflux
- PMID: 12370265
- PMCID: PMC151157
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI16391
Regulation and mechanisms of macrophage cholesterol efflux
Figures
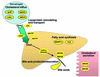


References
-
- Williams KJ, Tabas I. The response-to-retention hypothesis of atherogenesis reinforced. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1998;9:471–474. - PubMed
-
- Oram JF, Albers JJ, Cheung MC, Bierman EL. The effects of subfractions of high density lipoprotein on cholesterol efflux from cultured fibroblasts. Regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor activity. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:8348–8356. - PubMed
-
- Hara H, Yokoyama S. Interaction of free apolipoproteins with macrophages. Formation of high density lipoprotein-like lipoproteins and reduction of cellular cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:3080–3086. - PubMed
-
- Rubin EM, Krauss RM, Spangler EA, Verstuyft JG, Clift SM. Inhibition of early atherogenesis in transgenic mice by human apolipoprotein AI. Nature. 1991;353:265–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

