Differential requirement of SAGA components for recruitment of TATA-box-binding protein to promoters in vivo
- PMID: 12370284
- PMCID: PMC135674
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.21.7365-7371.2002
Differential requirement of SAGA components for recruitment of TATA-box-binding protein to promoters in vivo
Abstract
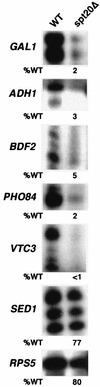
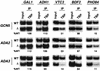
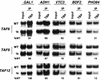
The multisubunit Saccharomyces cerevisiae SAGA (Spt-Ada-Gcn5-acetyltransferase) complex is required to activate transcription of a subset of RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. However, the contribution of each SAGA component to transcription activation is relatively unknown. Here, using a formaldehyde-based in vivo cross-linking and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, we have systematically analyzed the role of SAGA components in the recruitment of TATA-box binding protein (TBP) to SAGA-dependent promoters. We show that recruitment of TBP is diminished at a number of SAGA-dependent promoters in ada1delta, spt7delta, and spt20delta null mutants, consistent with previous biochemical data suggesting that these components maintain the integrity of the SAGA complex. We also find that Spt3p is generally required for TBP binding to SAGA-dependent promoters, consistent with biochemical and genetic experiments, suggesting that Spt3p interacts with and recruits TBP to the core promoter. By contrast, Spt8p, which has been proposed to be required for the interaction between Spt3p and TBP, is required for TBP binding at only a subset of SAGA-dependent promoters. Ada2p and Ada3p are both required for TBP recruitment to Gcn5p-dependent promoters, supporting previous biochemical data that Ada2p and Ada3p are required for the histone acetyltransferase activity of Gcn5p. Finally, our results suggest that TBP-associated-factor components of SAGA are differentially required for TBP binding to SAGA-dependent promoters. In summary, we show that SAGA-dependent promoters require different combinations of SAGA components for TBP recruitment, revealing a complex combinatorial network for transcription activation in vivo.
Figures

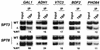
References
-
- Albright, S. R., and R. Tjian. 2000. TAFs revisited: more data reveal new twists and confirm old ideas. Gene 242:1-13. - PubMed
-
- Apone, L. M., C. A. Virbasius, F. C. Holstege, J. Wang, R. A. Young, and M. R. Green. 1998. Broad, but not universal, transcriptional requirement for yTAFII17, a histone H3-like TAFII present in TFIID and SAGA. Mol. Cell 2:653-661. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian, R., M. G. Pray-Grant, W. Selleck, P. A. Grant, and S. Tan. 2002. Role of the Ada2 and Ada3 transcriptional coactivators in histone acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:7989-7995. - PubMed
-
- Berger, S. L., B. Pina, N. Silverman, G. A. Marcus, J. Agapite, J. L. Regier, S. J. Triezenberg, and L. Guarente. 1992. Genetic isolation of ADA2: a potential transcriptional adaptor required for function of certain acidic activation domains. Cell 70:251-265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
