Identification, cDNA cloning, and targeted deletion of p70, a novel, ubiquitously expressed SH3 domain-containing protein
- PMID: 12370296
- PMCID: PMC135669
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.21.7491-7500.2002
Identification, cDNA cloning, and targeted deletion of p70, a novel, ubiquitously expressed SH3 domain-containing protein
Abstract
In a screen for proteins that interact with Jak2, we identified a previously uncharacterized 70-kDa protein and cloned the corresponding cDNA. The predicated sequence indicates that p70 contains an SH3 domain and a C-terminal domain with similarities to the catalytic motif of phosphoglycerate mutase. p70 transcripts were found in all tissues examined. Similarly, when an antibody raised against a C-terminal peptide to analyze p70 protein expression was used, all murine tissues examined were found to express p70. To investigate the in vivo role of p70, we generated a p70-deficient mouse strain. Mice lacking p70 are viable, develop normally, and do not display any obvious abnormalities. No differences were detected in various hematological parameters, including bone marrow colony-forming ability, in response to cytokines that utilize Jak2. In addition, no impairment in B- and T-cell development and proliferative ability was detected.
Figures







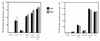
References
-
- Capecchi, M. R. 1994. Targeted gene replacement Sci. Am. 270:52-59. - PubMed
-
- Carter-Su, C., L. Rui, and M. R. Stofega. 2000. SH2-B and SIRP: JAK2 binding proteins that modulate the actions of growth hormone. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 55:293-311. - PubMed
-
- Damen, J. E., L. Liu, H. Wakao, A. Miyajima, P. Rosten, A. B. Jefferson, P. W. Majerus, J. Krosl, R. K. Humphries, and G. Krystal. 1997. The role of erythropoietin receptor tyrosine phosphorylation in erythropoietin-induced proliferation. Leukemia 3(Suppl.):423-425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
