Single molecule analysis of RNA polymerase elongation reveals uniform kinetic behavior
- PMID: 12370445
- PMCID: PMC129709
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.212358999
Single molecule analysis of RNA polymerase elongation reveals uniform kinetic behavior
Abstract
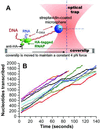
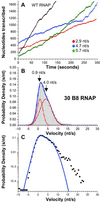
By using single-molecule measurements, we demonstrate that the elongation kinetics of individual Escherichia coli RNA polymerase molecules are remarkably homogeneous. We find no evidence of distinct elongation states among RNA polymerases. Instead, the observed heterogeneity in transcription rates results from statistical variation in the frequency and duration of pausing. When transcribing a gene without strong pause sites, RNA polymerase molecules display transient pauses that are distributed randomly in both time and distance. Transitions between the active elongation mode and the paused state are instantaneous within the resolution of our measurements (<1 s). This elongation behavior is compared with that of a mutant RNA polymerase that pauses more frequently and elongates more slowly than wild type.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

