How ions affect the structure of water
- PMID: 12371874
- PMCID: PMC1513647
- DOI: 10.1021/ja026014h
How ions affect the structure of water
Abstract
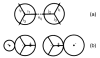
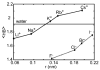
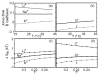
We model ion solvation in water. We use the MB model of water, a simple two-dimensional statistical mechanical model in which waters are represented as Lennard-Jones disks having Gaussian hydrogen-bonding arms. We introduce a charge dipole into MB waters. We perform (NPT) Monte Carlo simulations to explore how water molecules are organized around ions and around nonpolar solutes in salt solutions. The model gives good qualitative agreement with experiments, including Jones-Dole viscosity B coefficients, Samoilov and Hirata ion hydration activation energies, ion solvation thermodynamics, and Setschenow coefficients for Hofmeister series ions, which describe the salt concentration dependence of the solubilities of hydrophobic solutes. The two main ideas captured here are (1) that charge densities govern the interactions of ions with water, and (2) that a balance of forces determines water structure: electrostatics (water's dipole interacting with ions) and hydrogen bonding (water interacting with neighboring waters). Small ions (kosmotropes) have high charge densities so they cause strong electrostatic ordering of nearby waters, breaking hydrogen bonds. In contrast, large ions (chaotropes) have low charge densities, and surrounding water molecules are largely hydrogen bonded.
Figures









References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

