Comparative study of MR sialography and digital subtraction sialography for benign salivary gland disorders
- PMID: 12372736
- PMCID: PMC7976806
Comparative study of MR sialography and digital subtraction sialography for benign salivary gland disorders
Abstract
Background and purpose: MR sialography has become an alternative imaging technique for ductal salivary gland diseases. We compared the diagnostic accuracies of MR sialography and digital subtraction sialography in patients with successful completion of both examinations and benign salivary gland disorders.
Methods: In a prospective study, we attempted to examine salivary glands in 80 patients with clinically suspected diagnoses of sialadenitis and/or sialolithiasis. Each patient underwent digital subtraction sialography and MR sialography. MR sialography was obtained with a T2-weighted single-shot turbo spin-echo sequence (TR/TE 2800/1100 msec, acquisition time 7 seconds), with use of a quadrature head coil. Final diagnoses were confirmed by clinical follow-up and results of biopsy (n = 9) or surgery (n = 19).
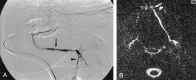
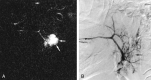
Results: Failure rate was 5% (four of 80) for MR sialography and 14% (11 of 80) for digital subtraction sialography. Eighty-one salivary glands (48 parotid, 33 submandibular) in 65 patients were successfully visualized with both modalities. MR sialography depicted the main ductal system and first- and second-order branches, whereas digital subtraction sialography was able to depict third-order branches. Sensitivity and specificity to diagnose chronic sialadenitis were 70% and 98% with MR and 96% and 100% with digital subtraction sialography. MR sialography enabled diagnosis of sialolithiasis with a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 98% versus 90% and 98% for each with digital subtraction sialography.
Conclusion: MR sialography with a heavily T2-weighted sequence is highly successful in the noninvasive visualization of the ductal system of major salivary glands. It is useful for diagnosing sialolithiasis and sialadenitis. Digital subtraction sialography, an invasive technique, had a substantial procedural failure rate, particularly for the submandibular duct. However, because of its higher spatial resolution, successfully completed digital subtraction sialography achieved superior diagnostic information compared with that of MR sialography.
Figures




References
-
- Rinast E, Gmelin E, Hollands-Thorn B. Digital subtraction sialography, conventional sialography, high resolution ultrasonography and computed tomography in the diagnosis of salivary gland diseases. Eur J Radiol 1989;9:224–230 - PubMed
-
- Gullotta U, Schekatz A. Digital subtraction sialography. Eur J Radiol 1983;33:339–340 - PubMed
-
- Yoshino N, Hosokawa A, Sasaki T, Yoshioka T. Interventional radiology for the nonsurgical removal of sialiths. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 1996;25:242–246 - PubMed
-
- Yousem DM, Kraut MA, Chalian AA. Major salivary gland imaging. Radiology 2000;216:19–29 - PubMed
-
- Murray ME, Buckenham TM, Joseph EA. The role of ultrasound in screening patients referred for sialography: a possible protocol. Clin Otolaryngol 1996;21:21–23 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
