Experimental cerebral fat embolism: embolic effects of triolein and oleic acid depicted by MR imaging and electron microscopy
- PMID: 12372741
- PMCID: PMC7976791
Experimental cerebral fat embolism: embolic effects of triolein and oleic acid depicted by MR imaging and electron microscopy
Abstract
Background and purpose: In fat embolism, free fatty acid is more toxic than neutral fat in terms of tissue damage. We evaluated the hyperacute embolic effects of triolein and oleic acid in cat brains by using MR imaging and electron microscopy.
Methods: T2-weighted imaging, diffusion-weighted imaging, and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging were performed in cat brains after the injection of triolein (group 1, n = 8) or oleic acid (group 2, n = 10) into the internal carotid artery. MR images were quantitatively assessed by comparing the signal intensity ratios of the lesions with their counterparts on T2-weighted images, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps, and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images. Electron microscopic findings in group 1 were compared with those in group 2.
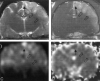
Results: Qualitatively, MR images revealed two types of lesions. Type 1 lesions were hyperintense on diffusion-weighted images and hypointense on ADC maps. Type 2 lesions were isointense or mildly hyperintense on diffusion-weighted images and isointense on ADC maps. Quantitatively, the signal intensity ratios of type 1 lesions in group 2 specimens were significantly higher on T2-weighted images (P =.013)/(P =.027) and lower on ADC maps compared with those of group 1. Electron microscopy of type 1 lesions in both groups revealed more prominent widening of the perivascular space and swelling of the neural cells in group 2, in contrast to notable endothelial defects in group 1.
Conclusion: MR and electron microscopic data on cerebral fat embolism induced by either triolein or oleic acid revealed characteristics suggestive of both vasogenic and cytotoxic edema in the hyperacute stage. Tissue damage appeared more severe in the oleic acid group than in the triolein group.
Figures








References
-
- Nakata Y, Tanaka H, Kuwagata Y, Yoshioka T, Sugimoto H. Triolein-induced pulmonary embolization and increased microvascular permeability in isolated perfused rat lungs. J Trauma 1999;47:111–119 - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Lee CH, Lee SH, et al. Early development of vasogenic edema in experimental cerebral fat embolism in cat. Invest Radiol 2001;36:460–469 - PubMed
-
- Fonte DA, Hausberger FX. Pulmonary free fatty acids in experimental fat embolism. J Trauma 1971;11:668–672 - PubMed
-
- Peltier LF. Fat embolism, III: the toxic properties of neutral fat and free fatty acids. Surgery 1956;40:665–670 - PubMed
-
- Hagerty CS. Experimental embolic glomerulonephritis produced with human fat, fatty acids and calcium soaps. Arch Pathol 1938;25:24–34
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
