Pre-spliceosome formation in S.pombe requires a stable complex of SF1-U2AF(59)-U2AF(23)
- PMID: 12374752
- PMCID: PMC129087
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf555
Pre-spliceosome formation in S.pombe requires a stable complex of SF1-U2AF(59)-U2AF(23)
Abstract
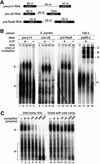
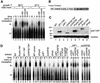
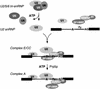
We have initiated a biochemical analysis of splicing complexes in extracts from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Extracts of S.pombe contain high levels of the spliceosome-like U2/5/6 tri-snRNP, which dissociates into mono-snRNPs in the presence of ATP, and supports binding of U2 snRNP to the 3' end of introns, yielding a weak ATP-independent E complex and the stable ATP-dependent complex A. The requirements for S.pombe complex A formation (pre-mRNA sequence elements, protein splicing factors, SF1/BBP and both subunits of U2AF) are analogous to those of mammalian complex A. The S.pombe SF1/BBP, U2AF(59) and U2AF(23) are tightly associated in a novel complex that is required for complex A formation. This pre-formed SF1- U2AF(59)-U2AF(23) complex may represent a streamlined mechanism for recognition of the branch site, pyrimidine tract and 3' splice site at the 3' end of introns.
Figures
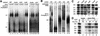



References
-
- Abovich N. and Rosbash,M. (1997) Cross-intron bridging interactions in the yeast commitment complex are conserved in mammals. Cell, 89, 403–412. - PubMed
-
- Bahler J., Wu,J.Q., Longtine,M.S., Shah,N.G., McKenzie,A.,III, Steever,A.B., Wach,A., Philippsen,P. and Pringle,J.R. (1998) Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast, 14, 943–951. - PubMed
-
- Beales M., Flay,N., McKinney,R., Habara,Y., Ohshima,Y., Tani,T. and Potashkin,J. (2000) Mutations in the large subunit of U2AF disrupt pre-mRNA splicing, cell cycle progression and nuclear structure. Yeast, 16, 1001–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

