Vibrio parahaemolyticus scrABC, a novel operon affecting swarming and capsular polysaccharide regulation
- PMID: 12374828
- PMCID: PMC135390
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.21.5946-5954.2002
Vibrio parahaemolyticus scrABC, a novel operon affecting swarming and capsular polysaccharide regulation
Abstract
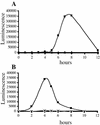
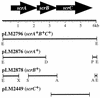
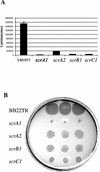
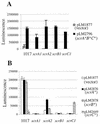
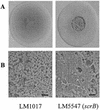
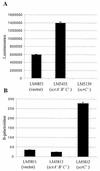
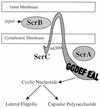
Swarming is an adaptation of many bacteria to growth on surfaces. A search for genes controlling swarmer cell differentiation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus identified a novel three-gene operon that potentially encodes a pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent enzyme, an extracellular solute-binding protein, and a membrane-bound GGDEF- and EAL-motif sensory protein. The functions of these motifs, which are named after conserved amino acid sequences, are unknown, although the domains are found singly and in combination in a variety of bacterial signaling proteins. Studies with translational fusions supported the predicted localization of the gene products. When the operon was overexpressed, swarmer cell gene transcription was induced in liquid culture. Mutants with defects in any of the three genes exhibited decreased swarming and lateral flagellar (laf) gene expression. Complementation studies confirmed an operon organization and suggested that all three genes participated in laf regulation. The lesions that decreased swarming increased capsular polysaccharide (CPS) production, and overexpression of the operon inhibited transcription of the CPS gene cpsA. Thus, the scrABC locus appears to inversely regulate two gene systems that are pertinent to colonization of surface swarming and CPS.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cyclic dimeric GMP signaling and regulation of surface-associated developmental programs.J Bacteriol. 2008 Feb;190(3):781-3. doi: 10.1128/JB.01852-07. Epub 2007 Dec 7. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18065536 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alexyev, M. F. 1995. Three kanamycin resistant gene cassettes with different polylinkers. BioTechniques 18:52-55. - PubMed
-
- Belas, R. 1996. Proteus mirabilis and other swarming bacteria, p. 183-219. In J. A. Shapiro and M. Dworkin (ed.), Bacteria as multicellular organisms. Oxford University Press, Oxford, England.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

