Soluble invertase expression is an early target of drought stress during the critical, abortion-sensitive phase of young ovary development in maize
- PMID: 12376627
- PMCID: PMC166589
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.005637
Soluble invertase expression is an early target of drought stress during the critical, abortion-sensitive phase of young ovary development in maize
Abstract
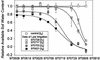
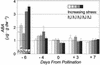
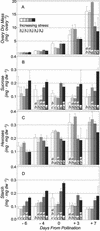
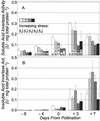
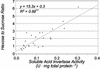
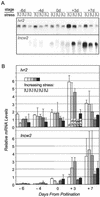
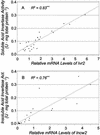
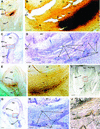
To distinguish their roles in early kernel development and stress, expression of soluble (Ivr2) and insoluble (Incw2) acid invertases was analyzed in young ovaries of maize (Zea mays) from 6 d before (-6 d) to 7 d after pollination (+7 d) and in response to perturbation by drought stress treatments. The Ivr2 soluble invertase mRNA was more abundant than the Incw2 mRNA throughout pre- and early post-pollination development (peaking at +3 d). In contrast, Incw2 mRNAs increased only after pollination. Drought repression of the Ivr2 soluble invertase also preceded changes in Incw2, with soluble activity responding before pollination (-4 d). Distinct profiles of Ivr2 and Incw2 mRNAs correlated with respective enzyme activities and indicated separate roles for these invertases during ovary development and stress. In addition, the drought-induced decrease and developmental changes of ovary hexose to sucrose ratio correlated with activity of soluble but not insoluble invertase. Ovary abscisic acid levels were increased by severe drought only at -6 d and did not appear to directly affect Ivr2 expression. In situ analysis showed localized activity and Ivr2 mRNA for soluble invertase at sites of phloem-unloading and expanding maternal tissues (greatest in terminal vascular zones and nearby cells of pericarp, pedicel, and basal nucellus). This early pattern of maternal invertase localization is clearly distinct from the well-characterized association of insoluble invertase with the basal endosperm later in development. This localization, the shifts in endogenous hexose to sucrose environment, and the distinct timing of soluble and insoluble invertase expression during development and stress collectively indicate a key role and critical sensitivity of the Ivr2 soluble invertase gene during the early, abortion-susceptible phase of development.
Figures

References
-
- Asch F, Andersen MN, Jensen CR, Mogensen VO. Ovary abscisic acid concentration does not induce kernel abortion in field-grown maize subjected to drought. Eur J Agron. 2001;15:119–129.
-
- Balk AB, de Boer AD. Rapid stalk elongation in tulip (Tulipa gesneriana L. cv. Apeldorn) and the combined action of cold-induced invertase and the water-channel protein γTIP. Planta. 1999;209:346–354. - PubMed
-
- Bassetti P, Westgate ME. Water deficit affects receptivity of maize silks. Crop Sci. 1993;33:279–282.
-
- Bassetti P, Westgate ME. Floral asynchrony and kernel set in maize quantified by image analysis. Agron J. 1994;86:699–703.
-
- Boyer JS. Advances in drought tolerance in plants. Adv Agron. 1996;56:187–218.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

