The predicted candidates of Arabidopsis plastid inner envelope membrane proteins and their expression profiles
- PMID: 12376647
- PMCID: PMC166609
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.008052
The predicted candidates of Arabidopsis plastid inner envelope membrane proteins and their expression profiles
Abstract
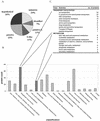
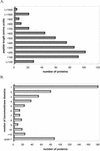
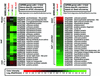
Plastid envelope proteins from the Arabidopsis nuclear genome were predicted using computational methods. Selection criteria were: first, to find proteins with NH(2)-terminal plastid-targeting peptides from all annotated open reading frames from Arabidopsis; second, to search for proteins with membrane-spanning domains among the predicted plastidial-targeted proteins; and third, to subtract known thylakoid membrane proteins. Five hundred forty-one proteins were selected as potential candidates of the Arabidopsis plastid inner envelope membrane proteins (AtPEM candidates). Only 34% (183) of the AtPEM candidates could be assigned to putative functions based on sequence similarity to proteins of known function (compared with the 69% function assignment of the total predicted proteins in the genome). Of the 183 candidates with assigned functions, 40% were classified in the category of "transport facilitation," indicating that this collection is highly enriched in membrane transporters. Information on the predicted proteins, tissue expression data from expressed sequence tags and microarrays, and publicly available T-DNA insertion lines were collected. The data set complements proteomic-based efforts in the increased detection of integral membrane proteins, low-abundance proteins, or those not expressed in tissues selected for proteomic analysis. Digital northern analysis of expressed sequence tags suggested that the transcript levels of most AtPEM candidates were relatively constant among different tissues in contrast to stroma and the thylakoid proteins. However, both digital northern and microarray analyses identified a number of AtPEM candidates with tissue-specific expression patterns.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of curated and predicted plastid subproteomes of Arabidopsis. Subcellular compartmentalization leads to distinctive proteome properties.Plant Physiol. 2004 Jun;135(2):723-34. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.040717. Plant Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15208420 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-scale proteomics reveals Arabidopsis thaliana gene models and proteome dynamics.Science. 2008 May 16;320(5878):938-41. doi: 10.1126/science.1157956. Epub 2008 Apr 24. Science. 2008. PMID: 18436743
-
The membrane proteome of stroma thylakoids from Arabidopsis thaliana studied by successive in-solution and in-gel digestion.Physiol Plant. 2015 Jul;154(3):433-46. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12308. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Physiol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25402197
-
European consortia building integrated resources for Arabidopsis functional genomics.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2003 Oct;6(5):426-9. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(03)00086-4. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2003. PMID: 12972042 Review.
-
Plant membrane proteomics.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2004 Dec;42(12):943-62. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2004.11.004. Epub 2005 Jan 18. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15707833 Review.
Cited by
-
Abundantly and rarely expressed Lhc protein genes exhibit distinct regulation patterns in plants.Plant Physiol. 2006 Mar;140(3):793-804. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.073304. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16524980 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroplast envelope membranes: a dynamic interface between plastids and the cytosol.Photosynth Res. 2007 May;92(2):225-44. doi: 10.1007/s11120-007-9195-8. Epub 2007 Jun 9. Photosynth Res. 2007. PMID: 17558548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis genes involved in acyl lipid metabolism. A 2003 census of the candidates, a study of the distribution of expressed sequence tags in organs, and a web-based database.Plant Physiol. 2003 Jun;132(2):681-97. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.022988. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12805597 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, Gene Structure, and Expression of BnMicEmUP: A Gene Upregulated in Embryogenic Brassica napus Microspores.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jan 11;11:576008. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.576008. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33519838 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiling of starch metabolism-related plastidic translocator genes in rice.Planta. 2006 Jan;223(2):248-57. doi: 10.1007/s00425-005-0128-5. Epub 2005 Dec 14. Planta. 2006. PMID: 16362329
References
-
- Adessi C, Miege C, Albrieux C, Rabilloud T. Two-dimensional electrophoresis of membrane proteins: a current challenge for immobilized pH gradients. Electrophoresis. 1997;18:127–135. - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408:796–813. - PubMed
-
- Audic S, Claverie JM. The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res. 1997;7:986–995. - PubMed
-
- Bannai H, Tamada Y, Maruyama O, Nakai K, Miyano S. Extensive feature detection of N-terminal protein sorting signals. Bioinformatics. 2002;18:298–305. - PubMed
-
- Block MA, Dorne AJ, Joyard J, Douce R. Preparation and characterization of membrane fractions enriched in outer and inner envelope membranes from spinach chloroplasts: I. Electrophoretic and immunochemical analyses. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:13273–13280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

