The abscisic acid-responsive kinase PKABA1 interacts with a seed-specific abscisic acid response element-binding factor, TaABF, and phosphorylates TaABF peptide sequences
- PMID: 12376648
- PMCID: PMC166610
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.001354
The abscisic acid-responsive kinase PKABA1 interacts with a seed-specific abscisic acid response element-binding factor, TaABF, and phosphorylates TaABF peptide sequences
Abstract
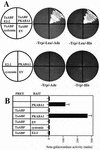
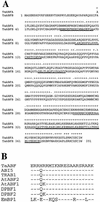
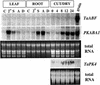
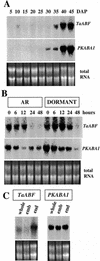
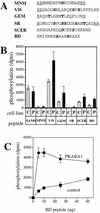
The abscisic acid (ABA)-induced protein kinase PKABA1 is present in dormant seeds and is a component of the signal transduction pathway leading to ABA-suppressed gene expression in cereal grains. We have identified a member of the ABA response element-binding factor (ABF) family of basic leucine zipper transcription factors from wheat (Triticum aestivum) that is specifically bound by PKABA1. This protein (TaABF) has highest sequence similarity to the Arabidopsis ABA response protein ABI5. In two-hybrid assays TaABF bound only to PKABA1, but not to a mutant version of PKABA1 lacking the nucleotide binding domain, suggesting that binding of TaABF requires prior binding of ATP as would be expected for binding of a protein substrate by a protein kinase. TaABF mRNA accumulated together with PKABA1 mRNA during wheat grain maturation and dormancy acquisition and TaABF transcripts increased transiently during imbibition of dormant grains. In contrast to PKABA1 mRNA, TaABF mRNA is seed specific and did not accumulate in vegetative tissues in response to stress or ABA application. PKABA1 produced in transformed cell lines was able to phosphorylate synthetic peptides representing three specific regions of TaABF. These data suggest that TaABF may serve as a physiological substrate for PKABA1 in the ABA signal transduction pathway during grain maturation, dormancy expression, and ABA-suppressed gene expression.
Figures

References
-
- Altshul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bethke PC, Schuurink R, Jones RL. Hormonal signalling in cereal aleurone. J Exp Bot. 1997;48:1337–1356.
-
- Bradford M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Busk PK, Pages M. Regulation of abscisic acid-induced transcription. Plant Mol Biol. 1998;37:425–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

