Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein, aP2, alters late atherosclerotic lesion formation in severe hypercholesterolemia
- PMID: 12377750
- PMCID: PMC4027051
- DOI: 10.1161/01.atv.0000033090.81345.e6
Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein, aP2, alters late atherosclerotic lesion formation in severe hypercholesterolemia
Abstract
Objective: The adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein, aP2, has important effects on insulin resistance, lipid metabolism, and atherosclerosis. Its expression in macrophages enhances early foam cell formation and atherosclerosis in vivo. This study was designed to determine whether aP2 deficiency has a similar effect in the setting of advanced atherosclerosis and severe hypercholesterolemia.
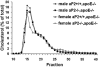
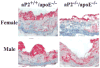
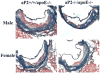
Methods and results: Mice deficient in aP2 and apolipoprotein E (aP2(-/-)apoE(-/-) mice) and apolipoprotein E-deficient control mice (apoE(-/-) mice) were fed a Western diet for 14 weeks. No significant differences in fasting serum levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, or free fatty acids were found between groups for each sex. Compared with apoE(-/-) control mice, male and female aP2(-/-)apoE(-/-) mice had significant reductions in mean atherosclerotic lesion size in the proximal aorta, en face aorta, and innominate/right carotid artery. Feeding the Western diet in the apoE-deficient background did not cause a significant reduction in insulin sensitivity in vivo, as determined by steady-state serum glucose levels and insulin tolerance testing.
Conclusions: These data demonstrate an important role for aP2 expression in the advanced stages of atherosclerotic lesion formation. Thus, aP2 provides an important physiological link between different features of the metabolic syndrome and is a potential target for therapy of atherosclerosis.
Figures
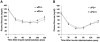
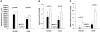
References
-
- Storch J, Thumser AE. The fatty acid transport function of fatty acid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1486:28–44. - PubMed
-
- Coe NR, Bernlohr DA. Physiological properties and functions of intracellular fatty acid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1391:287–306. - PubMed
-
- Distel RJ, Robinson GS, Spiegelman BM. Fatty acid regulation of gene expression: transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:5937–5941. - PubMed
-
- Chaput E, Saladin R, Silvestre M, Edgar AD. Fenofibrate and rosiglitazone lower serum triglycerides with opposing effects on body weight. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;271:445–450. - PubMed
-
- Melki SA, Abumrad NA. Expression of the adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein in streptozotocin-diabetes: effects of insulin deficiency and supplementation. J Lipid Res. 1993;34:1527–1534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

