Sonic hedgehog expression correlates with fundic gland differentiation in the adult gastrointestinal tract
- PMID: 12377798
- PMCID: PMC1773421
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.51.5.628
Sonic hedgehog expression correlates with fundic gland differentiation in the adult gastrointestinal tract
Abstract
Background: Sonic hedgehog (Shh) is an important endodermal morphogenetic signal during the development of the vertebrate gut. It controls gastrointestinal patterning in general, and gastric gland formation in particular. We have previously shown that Shh regulates gastric gland proliferation in the adult but detailed analysis of its expression along the adult gastrointestinal tract has never been undertaken. We therefore studied Shh expression along the normal human and rodent adult gastrointestinal tract as well as in intestinal metaplasia of the stomach, gastric and intestinal metaplasia of the oesophagus, and gastric heterotopia in Meckel's diverticulum.
Methods: The studies were performed with in situ hybridisation and by immunohistochemistry using an antibody that recognises the Shh precursor form.
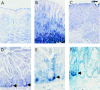
Results: We found that in the normal gastrointestinal tract, high levels of Shh were expressed in the fundic glands of the stomach. Shh expression was also found in fundic gland metaplasia and heterotopia. However, Shh expression was lost in intestinal metaplasia of the stomach.
Conclusion: We found a strong correlation between Shh expression and fundic gland differentiation. Our current study therefore provides evidence that in addition to its role in gastric epithelial development, Shh plays a unique role in gastric epithelial differentiation in adults.
Figures

References
-
- Hogan BLM. Morphogenesis. Cell 1999;96:225–33. - PubMed
-
- Nüsslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 1980;287:795–801. - PubMed
-
- Kalderon D. Transducing the hedgehog signal. Cell 2000;103:371–4. - PubMed
-
- Bitgood MJ, MacMahon AP. Hedgehog and Bmp genes are coexpressed at many diverse sites of cell-cell interaction in the mouse embryo. Dev Biol 1995;172:126–38. - PubMed
-
- Roberts DJ, Johnson RL, Burke AC, et al. Sonic hedgehog is an endodermal signal inducing BMP-4 and Hox genes during induction and regionalization of the chick hindgut. Development 1995;118:47–59. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
