Gastroprotective peptide trefoil factor family 2 gene is activated by upstream stimulating factor but not by c-Myc in gastrointestinal cancer cells
- PMID: 12377807
- PMCID: PMC1773432
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.51.5.685
Gastroprotective peptide trefoil factor family 2 gene is activated by upstream stimulating factor but not by c-Myc in gastrointestinal cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa results in the acute up-regulation of the trefoil factor family peptides TFF1, TFF2, and TFF3. They possess protective, healing, and tumour suppressive functions. Little is known about the regulation of TFF gene expression. The promoters of all three TFF genes contain binding sites (E box) for upstream stimulating factor (USF) and Myc/Max/Mad network proteins.
Aims: To determine the nature and function of transcription factors that bind to these E boxes and to understand their role for TFF gene expression.
Methods: TFF promoter activities were determined by reporter gene assays. DNA binding was monitored by electromobility shift assays and by chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses. Expression of endogenous TFF was determined by multiplex RT-PCR.
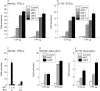
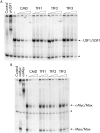
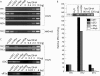
Results: It was observed that the TFF2 promoter is specifically and efficiently activated by USF transcription factors but not by c-Myc. USF displayed comparable binding to a high affinity Myc/Max binding site compared with the three TFF E boxes, while c-Myc exhibited lower affinity to the TFF E boxes. In contrast, pronounced binding differences were observed in cells with a strong preference for USF to interact specifically with the TFF2 E box, while Myc was not above background. Exogenous expression of USF was sufficient to activate the chromosomal TFF2 and to a lesser extent, the TFF1 gene.
Conclusion: These findings define USF factors as regulators of the TFF2 gene and suggest that promoter specific effects are important for a pronounced gene activation of this cytoprotective peptide.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 (winged helix domain) activates trefoil factor gene TFF1 through a binding motif adjacent to the TATAA box.DNA Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;18(2):157-64. doi: 10.1089/104454999315547. DNA Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10073575
-
Transcription factor GATA-6 activates expression of gastroprotective trefoil genes TFF1 and TFF2.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Feb 29;1490(3):324-32. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(00)00013-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10684977
-
[Trefoil factor family gene and peptide expression in pterygium].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2003 Dec;26(10):1007-14. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2003. PMID: 14691392 French.
-
Trefoil factors and human gastric cancer (review).Int J Mol Med. 2003 Jul;12(1):3-9. Int J Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 12792801 Review.
-
Cell type specific expression of secretory TFF peptides: colocalization with mucins and synthesis in the brain.Int Rev Cytol. 2002;213:147-81. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(02)13014-2. Int Rev Cytol. 2002. PMID: 11837892 Review.
Cited by
-
Trefoil Factor Family Member 2: From a High-Fat-Induced Gene to a Potential Obesity Therapy Target.Metabolites. 2021 Aug 12;11(8):536. doi: 10.3390/metabo11080536. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34436477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upstream stimulatory factor 1 activates GATA5 expression through an E-box motif.Biochem J. 2012 Aug 15;446(1):89-98. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111942. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22625849 Free PMC article.
-
Human Trefoil Factor 3 induces the transcription of its own promoter through STAT3.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 25;6:30421. doi: 10.1038/srep30421. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27453253 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of confluence-dependent expression of CD26 in colon cancer cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2011 Feb 1;11:51. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-51. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21284881 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of the human trefoil factor 3 gene promoter.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 17;9(4):e95562. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095562. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24743382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uchino H, Kataoka H, Itoh H, et al. Overexpression of intestinal trefoil factor in human colon carcinoma cells reduces cellular growth in vitro and in vivo. Gastroenterology 2000;118:60–9. - PubMed
-
- Playford RJ, Marchbank T, Chinery R et al. Human spasmolytic polypeptide is a cytoprotective agent that stimulates cell migration. Gastroenterology 1995;108:108–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
