The effects of vitamin E succinate on the expression of c-jun gene and protein in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells
- PMID: 12378615
- PMCID: PMC4656561
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.782
The effects of vitamin E succinate on the expression of c-jun gene and protein in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of vitamin E succinate (VES) on the expression of c-jun gene and protein in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells.
Methods: After SGC-7901 cells were treated with VES at different doses (5,10,20 mg x L(-1)) at different time, reverse transcription-PCR technique was used to detect the level of c-jun mRNA; Western Blot was applied to measure the expression of c-jun protein.
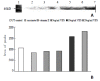
Results: After the cells were treated with VES at 20 mg x L(-1) for 3 h, the expression rapidly reached its maximum that was 3.5 times of UT control (P<0.01). The level of c-jun mRNA was also increased following treatment of VES for 6 h. However,the expression after treatment of VES at 5 mg x L(-1) for 24 h was 1.6 times compared with UT control (P<0.01). Western blot analysis showed that the level of c-jun protein was obviously elevated in VES-treated SGC-7901 cells at 20 mg x L(-1) for 3 h. The expression of c-jun protein was gradually increased after treatment of VES at 20 mg x L(-1) for 3, 6, 12 and 24 h, respectively, with an evident time-effect relationship.
Conclusion: The levels of c-jun mRNA and protein in VES-treated SGC-7901 cells were increased in a dose- and time-dependent manner; the expression of c-jun was prolonged by VES, indicating that c-jun is involved in VES-induced apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for vitamin E succinate-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Apr 15;10(8):1110-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1110. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15069708 Free PMC article.
-
RRR-alpha-tocopheryl succinate inhibits human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell growth by inducing apoptosis and DNA synthesis arrest.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Feb;8(1):26-30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i1.26. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 11833065 Free PMC article.
-
RRR-alpha-tocopheryl succinate inhibits EL4 thymic lymphoma cell growth by inducing apoptosis and DNA synthesis arrest.Nutr Cancer. 1997;27(1):92-101. doi: 10.1080/01635589709514508. Nutr Cancer. 1997. PMID: 8970189
-
Roles of Fas signaling pathway in vitamin E succinate-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Dec;8(6):982-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.982. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 12439910 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of activator protein-1 (AP-1) in induction of apoptosis by vitamin E succinate in human breast cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 1997 Jul;19(3):180-90. Mol Carcinog. 1997. PMID: 9254885
Cited by
-
Cloning of human 15ku selenoprotein gene from H9 T cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Aug;9(8):1777-80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1777. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12918119 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for vitamin E succinate-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Apr 15;10(8):1110-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1110. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15069708 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and identification of mimotope of gastric cancer associated antigen MGb1-Ag.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Sep;9(9):1920-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1920. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12970876 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of vitamin E succinate on the expression of Fas and PCNA proteins in human gastric carcinoma cells and its clinical significance.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Apr 1;10(7):945-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i7.945. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15052671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fariss MW, Fortuna MB, Everett CK, Smith JD, Trent DF, Djuric Z. The selective antiproliferative effects of alpha-tocopheryl hemisuccinate and cholesteryl hemisuccinate on murine leukemia cells result from the action of the intact compounds. Cancer Res. 1994;54:3346–3351. - PubMed
-
- Ottino P, Duncan JR. Effect of alpha-tocopherol succinate on free radical and lipid peroxidation levels in BL6 melanoma cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997;22:1145–1151. - PubMed
-
- Israel K, Sanders BG, Kline K. RRR-alpha-tocopheryl succinate inhibits the proliferation of human prostatic tumor cells with defective cell cycle/differentiation pathways. Nutr Cancer. 1995;24:161–169. - PubMed
-
- Turley JM, Ruscetti FW, Kim SJ, Fu T, Gou FV, Birchenall-Roberts MC. Vitamin E succinate inhibits proliferation of BT-20 human breast cancer cells: increased binding of cyclin A negatively regulates E2F transactivation activity. Cancer Res. 1997;57:2668–2675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

