Association of hTcf-4 gene expression and mutation with clinicopathological characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 12378619
- PMCID: PMC4656565
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.804
Association of hTcf-4 gene expression and mutation with clinicopathological characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: Hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) is a significant health problem in China. But the molecular mechanisms of HCC remains unclear. APC/beta-Catenin/Tcf signaling pathway, also known as Wnt pathway, plays a critical role in the development and oncogenesis. As little is known about the alteration of human T-cell transcription factor-4 (hTcf-4) gene in HCC, it is of interest to study the expression and mutation of hTcf-4 gene in HCC and the relationship between hTcf-4 gene and progression of HCC.
Methods: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method was used to detect the expression of hTcf-4 mRNA in 32 HCC and para-cancerous tissues and 5 normal liver tissues. PCR-single strand conformation polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) method was used to detect the mutation of hTcf-4 exons 1, 4, 9 and 15 in HCC. The correlation of expression and mutation of the hTcf-4 gene with clinicopathological characteristics of HCC was also analyzed.
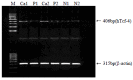
Results: RT-PCR showed that the expression rate of hTcf-4 mRNA in HCC, para-cancerous tissues and normal liver tissues was 90.6 %, 71.9 % and 80 %, respectively. The gene expression level in tumor was 0.71+/-0.13, much higher than that in para-cancerous liver 0.29+/-0.05 and normal liver 0.26+/-0.05 (P<0.001), although there was no significant difference in gene expression level between para-cancerous tissues and normal liver (P>0.05). Furthermore, hTcf-4 gene expression was closely associated with tumor capsule status and intrahepatic metastasis of HCC. On SSCP, 2 of 32 cases of HCC (6.25 %) displayed characteristic mutational mobility shifts in exon 15 of the hTcf-4 gene. No abnormal shifting bands were observed in para-cancerous tissues.
Conclusion: The high expression level of hTcf-4 in HCC, especially in tumors with metastasis, suggests that the over-expression of hTcf-4 gene may be closely associated with development and progression of HCC, but the mutation of this gene seemed to play less important role in this respect.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Abnormal beta-catenin gene expression with invasiveness of primary hepatocellular carcinoma in China.World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Aug;7(4):542-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i4.542. World J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11819825 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of mutation and expression of beta-catenin, T-cell factor-4 and glycogen synthase kinase 3-beta genes.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003 Mar;18(3):280-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.02973.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003. PMID: 12603528
-
Mutation and overexpression of the beta-catenin gene may play an important role in primary hepatocellular carcinoma among Chinese people.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2001 Sep;127(9):577-81. doi: 10.1007/s004320100259. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11570580 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of aberrant Wnt signaling in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 28;21(20):6317-28. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6317. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26034368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular signatures of noncancerous liver tissue can predict the risk for late recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastroenterol. 2010 Feb;45(2):146-52. doi: 10.1007/s00535-009-0164-1. Epub 2009 Dec 8. J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 19997856 Review.
Cited by
-
Replication study for the association of TCF7L2 with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a Japanese population.Diabetologia. 2007 May;50(5):980-4. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0618-z. Epub 2007 Mar 6. Diabetologia. 2007. PMID: 17340123
-
Roles of β-catenin, TCF-4, and survivin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: correlation with clinicopathological features and prognostic significance.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Feb 28;19:48. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0764-7. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 30867651 Free PMC article.
-
Dickkopfs and Wnt/β-catenin signalling in liver cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2011 Aug 10;2(8):311-25. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i8.311. World J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21876852 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense Tcf inhibits the neoplastic growth of liver cancer cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004 Nov;130(11):671-8. doi: 10.1007/s00432-004-0580-9. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15221470 Free PMC article.
-
TCF 4 tumor suppressor: a molecular target in the prognosis of sporadic colorectal cancer in humans.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020 Mar 31;25:24. doi: 10.1186/s11658-020-00217-w. eCollection 2020. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32265994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smalley MJ, Dale TC. Wnt signalling in mammalian development and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1999;18:215–230. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, Morin PJ, Clevers H. The Yin-Yang of TCF/beta-catenin signaling. Adv Cancer Res. 2000;77:1–24. - PubMed
-
- Rubinfeld B, Albert I, Porfiri E, Fiol C, Munemitsu S, Polakis P. Binding of GSK3beta to the APC-beta-catenin complex and regulation of complex assembly. Science. 1996;272:1023–1026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

