Apoptosis of hepatoma cells SMMC-7721 induced by Ginkgo biloba seed polysaccharide
- PMID: 12378625
- PMCID: PMC4656570
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.832
Apoptosis of hepatoma cells SMMC-7721 induced by Ginkgo biloba seed polysaccharide
Abstract
Aim: To study the apoptosis of hepatoma cells SMMC-7721 induced by polysaccharide isolated from Ginkgo biloba seed.
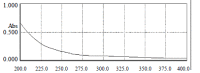
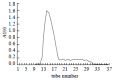
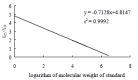
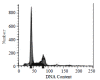
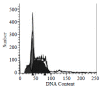
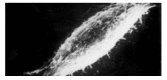
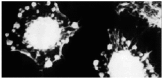
Methods: Ginkgo biloba seed polysaccharide (GBSP) was isolated by ethanol fractionation of Ginkgo biloba seed and purified by Sephadex G-200 chromatography. The purity of GBSP was verified by reaction with iodine-potassium iodide and ninhydrin and confirmed by UV spectrophotometer, cellulose acetate membrane electrophoresis and Sepharose 4B gel filtration chromatography. The Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Flow Cytometry (FCM) were used to examine the SMMC-7721 cells with and without GBSP treatment at 500 mg/ml for 36 h.
Results: GBSP product obtained was of high purity with the average molecular weight of 1.86 X 10(5). Quantitative analysis of SMMC-7721 cells in vitro with FCM showed that the percentages of G(2)-M cells without and with GBSP treatment were 17.01+/-1.28 % and 11.77+/-1.50% (P<0.05), the debris ratio of the cells were 0.46+/-0.12 % and 0.06+/-0.06 % (P<0.01), and the apoptosis ratio of cells was 3.84+/-0.55 % and 9.13+/-1.48 % (P<0.01) respectively. Following GBSP treatment, microvilli of SMMC-7721 cells appeared thinner and the number of spherical cells increased markedly. Most significantly, the apoptosis bodies were formed on and around the spherical cells treated with GBSP.
Conclusion: GBSP could potentially induce the apoptosis of SMMC-7721 cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural characterization of a α-d-glucan from Ginkgo biloba seeds and its protective effects on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice.Carbohydr Polym. 2025 Feb 1;349(Pt B):123022. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.123022. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Carbohydr Polym. 2025. PMID: 39638527
-
Purification and characterization of a novel ~18 kDa antioxidant protein from Ginkgo biloba seeds.Molecules. 2012 Dec 11;17(12):14778-94. doi: 10.3390/molecules171214778. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 23519252 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison in bioactivity and characteristics of Ginkgo biloba seed polysaccharides from four extract pathways.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Sep 15;159:1156-1164. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.129. Epub 2020 May 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32442575
-
Ginkgo biloba seed exocarp: A waste resource with abundant active substances and other components for potential applications.Food Res Int. 2022 Oct;160:111637. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111637. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36076439 Review.
-
[Food Poisoning by Ginkgo Seeds through Vitamin B6 Depletion].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):1-6. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00136. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606915 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
PPARgamma pathway activation results in apoptosis and COX-2 inhibition in HepG2 cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Jun;9(6):1220-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1220. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12800228 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic effect of Ginkgo biloba kernel extract on HCT116 and A2058 cancer cell lines.Heliyon. 2020 Sep 19;6(9):e04941. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04941. eCollection 2020 Sep. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33005784 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental study of anti-tumor effects of polysaccharides from Angelica sinensis.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Sep;9(9):1963-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1963. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12970885 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of ginkgol C17:1 on cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity: Protecting human normal L02 hepatocytes versus sensitizing human hepatoma HepG2 cells.Oncol Lett. 2019 Mar;17(3):3181-3190. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.9974. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30867748 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ginkgol C17:1 on cisplatin-induced autophagy and apoptosis in HepG2 cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jan;15(1):1021-1029. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7398. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29399162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liebgott T, Miollan M, Berchadsky Y, Drieu K, Culcasi M, Pietri S. Complementary cardioprotective effects of flavonoid metabolites and terpenoid constituents of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) during ischemia and reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol. 2000;95:368–377. - PubMed
-
- Bastianetto S, Zheng WH, Quirion R. The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects and rescues hippocampal cells against nitric oxide-induced toxicity: involvement of its flavonoid constituents and protein kinase C. J Neurochem. 2000;74:2268–2277. - PubMed
-
- Kim SJ, Lim MH, Chun IK, Won YH. Effects of flavonoids of Ginkgo biloba on proliferation of human skin fibroblast. Skin Pharmacol. 1997;10:200–205. - PubMed
-
- Wójcicki J, Gawrońska-Szklarz B, Bieganowski W, Patalan M, Smulski HK, Samochowiec L, Zakrzewski J. Comparative pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of flavonoid glycosides of Ginkgo biloba after a single oral administration of three formulations to healthy volunteers. Mater Med Pol. 1995;27:141–146. - PubMed
-
- Oyama Y, Fuchs PA, Katayama N, Noda K. Myricetin and quercetin, the flavonoid constituents of Ginkgo biloba extract, greatly reduce oxidative metabolism in both resting and Ca (2+)-loaded brain neurons. Brain Res. 1994;635:125–129. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

