Nitric oxide limits the expansion of antigen-specific T cells in mice infected with the microfilariae of Brugia pahangi
- PMID: 12379675
- PMCID: PMC130375
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.5997-6004.2002
Nitric oxide limits the expansion of antigen-specific T cells in mice infected with the microfilariae of Brugia pahangi
Abstract
Infection of BALB/c mice with the microfilariae (Mf) of the filarial nematode Brugia pahangi results in an antigen-specific proliferative defect that is induced by high levels of NO. Using carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimydl ester and cell surface labeling, it was possible to identify a population of antigen-specific T cells from Mf-infected BALB/c mice that expressed particularly high levels of CD4 (CD4(hi)). These cells proliferated in culture only when inducible NO synthase was inhibited and accounted for almost all of the antigen-specific proliferative response under those conditions. CD4(hi) cells also expressed high levels of CD44, consistent with their status as activated T cells. A similar population of CD4(hi) cells was observed in cultures from Mf-infected gamma interferon receptor knockout (IFN-gammaR(-/-)) mice. Terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling staining revealed that the CD4(+) T cells from Mf-infected wild-type mice were preferentially susceptible to apoptosis compared to CD4(+) T cells from IFN-gammaR(-/-) mice. These studies suggest that the expansion of antigen-specific T cells in Mf-infected mice is limited by NO.
Figures
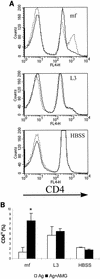



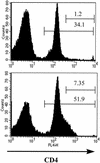

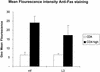
References
-
- Allen, J. E., R. A. Lawrence, and R. M. Maizels. 1996. APC from mice harbouring the filarial parasite, Brugia malayi, prevent cellular proliferation but not cytokine production. Int. Immunol. 8:143-151. - PubMed
-
- Allen, J. E., and P. Loke. 2001. Divergent roles for macrophages in lymphatic filariasis. Parasite Immunol. 23:345-352. - PubMed
-
- Blass, S. L., E. Pure, and C. A. Hunter. 2001. A role for CD44 in the production of IFN-γ and immunopathology during infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 166:5726-5732. - PubMed
-
- Chen, D., R. J. McKallip, A. Zeytun, Y. Do, C. Lombard, J. L. Robertson, T. W. Mak, P. S. Nagarkatti, and M. Nagarkatti. 2001. CD44-deficient mice exhibit enhanced hepatitis after concanavilin A injection: evidence for involvement of CD44 in activation-induced cell death. J. Immunol. 166:5889-5897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

