Divergent role of gamma interferon in a murine model of pulmonary versus systemic Klebsiella pneumoniae infection
- PMID: 12379710
- PMCID: PMC130357
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.6310-6318.2002
Divergent role of gamma interferon in a murine model of pulmonary versus systemic Klebsiella pneumoniae infection
Abstract
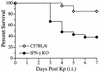
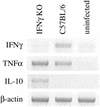
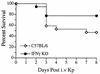
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a leading cause of both community-acquired and nosocomial gram-negative-bacterial pneumonia. A further clinical complication of pulmonary K. pneumoniae infection is dissemination of bacteria from the lung into the peripheral blood, resulting in bacteremia concurrent with the localized pulmonary infection. Here, we report studies detailing the divergent role of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) in pulmonary versus systemic K. pneumoniae infection. Intratracheal inoculation of IFN-gamma knockout mice resulted in significantly increased mortality compared to that observed for wild-type infected animals. Increased mortality correlated with a 100-fold increase in pulmonary bacteria within 2 days postinfection and upregulation of lung-associated interleukin-10 (IL-10) mRNA. Interestingly, IFN-gamma knockout mice had a twofold reduction in plasma aminospartate transferase activity, indicating diminished liver injury following peripheral blood bacterial dissemination. To study the host response towards blood-borne bacteria in the absence of the ongoing pulmonary infection, intravenous inoculation studies were initiated. IFN-gamma knockout mice were no more susceptible to intravenous infection than their wild-type counterparts. The consistent observation in IFN-gamma knockout mice was for improved survival correlating with increased clearance of blood- and liver-associated bacteria. Intravenous inoculation resulted in a two- to threefold increase in hepatic IL-10 production 24 and 48 h postinfection. Liver injury was also significantly reduced in IFN-gamma knockout mice. These data indicate that IFN-gamma secretion is a critical mediator in the resolution of localized gram-negative pulmonary pneumonia. Surprisingly, host responses towards systemic infection with the same bacteria appear to be IFN-gamma independent.
Figures

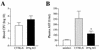



References
-
- Boehm, U., T. Klamp, M. Groot, and J. C. Howard. 1997. Cellular responses to interferon-gamma. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15:749-795. - PubMed
-
- Burwen, D. R., S. N. Banerjee, and R. P. Gaynes. 1994. Ceftazidime resistance among selected nosocomial gram-negative bacilli in the United States. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. J. Infect. Dis. 170:1622-1625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

