Modulation of cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration in airway epithelial cells by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 12379720
- PMCID: PMC130342
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.6399-6408.2002
Modulation of cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration in airway epithelial cells by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
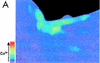
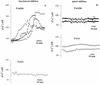
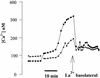
Modulation of cytosolic (intracellular) Ca(2+) concentration (Ca(i)) may be an important host response when airway epithelial cells are exposed to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. We measured Ca(i) in Calu-3 cells exposed from the apical or basolateral surface to cytotoxic and noncytotoxic strains of P. aeruginosa. Apical addition of either noncytotoxic strains or cytotoxic strains failed to affect Ca(i) over a 3-h time period, nor were changes observed after basolateral addition of noncytotoxic strains. In contrast, basolateral addition of cytotoxic strains caused a slow increase in Ca(i) from 100 nM to 200 to 400 nM. This increase began after 20 to 50 min and persisted for an additional 30 to 75 min, at which time the cells became nonviable. P. aeruginosa-induced increases in Ca(i) were blocked by the addition of the Ca channel blocker La(3+) to the basolateral but not to the apical chamber. Likewise, replacing the basolateral but not the apical medium with Ca-free solution prevented P. aeruginosa-mediated changes in Ca(i). With isogenic mutants of PA103, we demonstrated that the type III secretion apparatus, the type III-secreted effector ExoU, and type IV pili were necessary for increased Ca(i). We propose that translocation of ExoU through the basolateral surface of polarized airway epithelial cells via the type III secretion apparatus leads to release of Ca stored in the endoplasmic reticulum and activation of Ca channels in the basolateral membranes of epithelial cells.
Figures





References
-
- Aderem, A., and R. J. Ulevitch. 2000. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 406:782-787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

