Evidence inconsistent with a negative influence of T helper 2 cells on protection afforded by a dominant T helper 1 response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis lung infection in mice
- PMID: 12379724
- PMCID: PMC130368
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.6436-6443.2002
Evidence inconsistent with a negative influence of T helper 2 cells on protection afforded by a dominant T helper 1 response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis lung infection in mice
Abstract
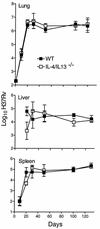
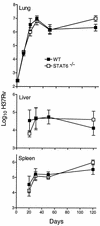
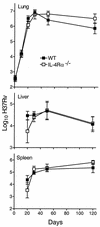
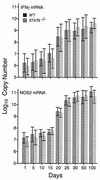
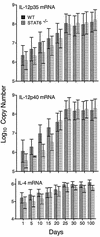
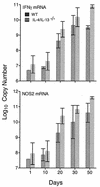
Mice incapable of generating an efficient Th2 response because of functional deletion of the genes for signal transducer and activation of transcription 6 (Stat6), interleukin-4 receptor alpha chain (IL-4Ralpha), or IL-4 plus IL-13 (IL-4/IL-13) were no more resistant than wild-type (WT) mice to airborne infection with virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. WT mice were able to control infection and hold it at a stationary level following 20 days of log linear M. tuberculosis growth. Likewise, infection was kept under control and was held at the same stationary level in IL-4/IL-13(-/-) mice but progressed to a slightly higher level in Stat6(-/-) and IL-4Ralpha(-/-) mice. The onset of stationary-level infection in WT mice was associated with the expression of Th1-mediated immunity, as evidenced by an approximately 100- to 1,000-fold increase in the lungs in the synthesis of mRNA for IL-12, gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2) that was sustained for at least 100 days. IL-12 is essential for the induction of Th1 immunity, IFN-gamma is a key Th1 cytokine involved in mediation of immunity, and NOS2 is an inducible enzyme of macrophages and is needed by these cells to express immunity. In response to infection, the lungs of Stat6(-/-) mice showed increases in synthesis of mRNA for IL-12, IFN-gamma, and NOS2 similar to that seen in WT mice. In IL-4/IL-13(-/-) mice, however, synthesis of mRNA for IFN-gamma and NOS2 reached higher levels than in WT mice. These results argue against the notion that a Th2 response is partly or wholly responsible for the inability of Th1-mediated immunity to resolve infection with a virulent strain of M. tuberculosis.
Figures
References
-
- Baliko, Z., L. Szereday, and J. Szekeres-Bartho. 1998. Th2 biased immune response in cases with active Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and tuberculin anergy. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 22:199-204. - PubMed
-
- Boom, W. H. 1996. The role of T cell subsets in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Infect. Agents Dis. 5:73-81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

