ARFGAP1 promotes the formation of COPI vesicles, suggesting function as a component of the coat
- PMID: 12379802
- PMCID: PMC2173491
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200206015
ARFGAP1 promotes the formation of COPI vesicles, suggesting function as a component of the coat
Abstract
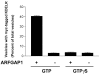
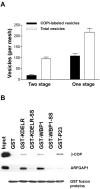
The role of GTPase-activating protein (GAP) that deactivates ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1) during the formation of coat protein I (COPI) vesicles has been unclear. GAP is originally thought to antagonize vesicle formation by triggering uncoating, but later studies suggest that GAP promotes cargo sorting, a process that occurs during vesicle formation. Recent models have attempted to reconcile these seemingly contradictory roles by suggesting that cargo proteins suppress GAP activity during vesicle formation, but whether GAP truly antagonizes coat recruitment in this process has not been assessed directly. We have reconstituted the formation of COPI vesicles by incubating Golgi membrane with purified soluble components, and find that ARFGAP1 in the presence of GTP promotes vesicle formation and cargo sorting. Moreover, the presence of GTPgammaS not only blocks vesicle uncoating but also vesicle formation by preventing the proper recruitment of GAP to nascent vesicles. Elucidating how GAP functions in vesicle formation, we find that the level of GAP on the reconstituted vesicles is at least as abundant as COPI and that GAP binds directly to the dilysine motif of cargo proteins. Collectively, these findings suggest that ARFGAP1 promotes vesicle formation by functioning as a component of the COPI coat.
Figures






References
-
- Antonny, B., D. Madden, S. Hamamoto, L. Orci, and R. Schekman. 2001. Dynamics of the COPII coat with GTP and stable analogues. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:531–537. - PubMed
-
- Aoe, T., I. Huber, C. Vasudevan, S.C. Watkins, G. Romero, D. Cassel, and V.W. Hsu. 1999. The KDEL receptor regulates the in vivo activity of a GTPase-activating protein for ARF1 by interacting with its non-catalytic domain. J. Biol. Chem. 274:20545–20549. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe, C., L. Orci, T. Yeung, M. Hosobuchi, S. Hamamoto, N. Salama, M.F. Rexach, M. Ravazzola, M. Amherdt, and R. Schekman. 1994. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 77:895–907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

