Myogenic specification of side population cells in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 12379804
- PMCID: PMC2173497
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200202092
Myogenic specification of side population cells in skeletal muscle
Abstract
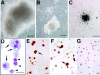
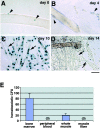
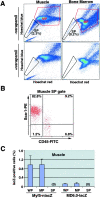
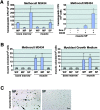
Skeletal muscle contains myogenic progenitors called satellite cells and muscle-derived stem cells that have been suggested to be pluripotent. We further investigated the differentiation potential of muscle-derived stem cells and satellite cells to elucidate relationships between these two populations of cells. FACS(R) analysis of muscle side population (SP) cells, a fraction of muscle-derived stem cells, revealed expression of hematopoietic stem cell marker Sca-1 but did not reveal expression of any satellite cell markers. Muscle SP cells were greatly enriched for cells competent to form hematopoietic colonies. Moreover, muscle SP cells with hematopoietic potential were CD45 positive. However, muscle SP cells did not differentiate into myocytes in vitro. By contrast, satellite cells gave rise to myocytes but did not express Sca-1 or CD45 and never formed hematopoietic colonies. Importantly, muscle SP cells exhibited the potential to give rise to both myocytes and satellite cells after intramuscular transplantation. In addition, muscle SP cells underwent myogenic specification after co-culture with myoblasts. Co-culture with myoblasts or forced expression of MyoD also induced muscle differentiation of muscle SP cells prepared from mice lacking Pax7 gene, an essential gene for satellite cell development. Therefore, these data document that satellite cells and muscle-derived stem cells represent distinct populations and demonstrate that muscle-derived stem cells have the potential to give rise to myogenic cells via a myocyte-mediated inductive interaction.
Figures
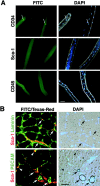
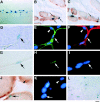
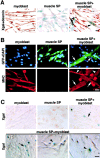
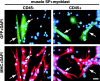
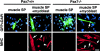
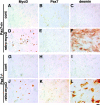
References
-
- Asakura, A., G.E. Lyons, and S.J. Tapscott. 1995. The regulation of MyoD gene expression: conserved elements mediate expression in embryonic axial muscle. Dev. Biol. 171:386–398. - PubMed
-
- Asakura, A., M. Komaki, and M. Rudnicki. 2001. Muscle satellite cells are multipotential stem cells that exhibit myogenic, osteogenic, and adipogenic differentiation. Differentiation. 68:245–253. - PubMed
-
- De Angelis, L., L. Berghella, M. Coletta, L. Lattanzi, M. Zanchi, M.G. Cusella-De Angelis, C. Ponzetto, and G. Cossu. 1999. Skeletal myogenic progenitors originating from embryonic dorsal aorta coexpress endothelial and myogenic markers and contribute to postnatal muscle growth and regeneration. J. Cell Biol. 147:869–878. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

