Direct inhibition by cannabinoids of human 5-HT3A receptors: probable involvement of an allosteric modulatory site
- PMID: 12381672
- PMCID: PMC1573528
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704829
Direct inhibition by cannabinoids of human 5-HT3A receptors: probable involvement of an allosteric modulatory site
Abstract
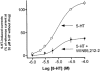
Excised outside-out patches from HEK293 cells stably transfected with the human (h) 5-HT3A receptor cDNA were used to determine the effects of cannabinoid receptor ligands on the 5-HT-induced current using the patch clamp technique. In addition, binding studies with radioligands for 5-HT3 as well as for cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors were carried out. The 5-HT-induced current was inhibited by the following cannabinoid receptor agonists (at decreasing order of potency): 9-THC, WIN55,212-2, anandamide, JWH-015 and CP55940. The WIN55,212-2-induced inhibition was not altered by SR141716A, a CB1 receptor antagonist. WIN55,212-3, an enantiomer of WIN55,212-2, did not affect the 5-HT-induced current. WIN55,212-2 did not change the EC50 value of 5-HT in stimulating current, but reduced the maximum effect. The CB1 receptor ligand [3H]-SR141716A and the CB1/CB2 receptor ligand [3H]-CP55940 did not specifically bind to parental HEK293 cells. In competition experiments on membranes of HEK293 cells transfected with the h5-HT3A receptor cDNA, WIN55,212-2, CP55940, anandamide and SR141716A did not affect [3H]-GR65630 binding, but 5-HT caused a concentration dependent-inhibition. In conclusion, cannabinoids stereoselectively inhibit currents through recombinant h5-HT3A receptors independently of cannabinoid receptors. Probably the cannabinoids act allosterically at a modulatory site of the h5-HT3A receptor. Thus the functional state of the receptor can be controlled by the endogenous ligand anandamide. This site is a potential target for new analgesic and antiemetic drugs.
Figures




References
-
- AAPRO M.S. 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. An overview of their present status and future potential in cancer therapy-induced emesis. Drugs. 1991;42:551–568. - PubMed
-
- ABOOD M.E., MARTIN B.R. Neurobiology of marijuana abuse. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1992;13:201–206. - PubMed
-
- AMERI A. The effects of cannabinoid on the brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999;58:315–348. - PubMed
-
- BARANN M., MOLDERINGS G., URBAN B.W., GÖTHERT M.Inhibition by cannabinoid1 receptor agonists of currents through human 5-HT3A receptors Soc. Neurosci. 2001272126abstract
-
- BARANN M., MEDER W., DORNER Z., BRÜSS M., BÖNISCH H., GÖTHERT M., URBAN B.W. Recombinant human 5-HT3A receptors in outside-out patches of HEK293 cells: basic properties and barbiturate effects. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 2000;362:255–265. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

