Involvement of tissue kallikrein but not plasma kallikrein in the development of symptoms mediated by endogenous kinins in acute pancreatitis in rats
- PMID: 12381683
- PMCID: PMC1573532
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704910
Involvement of tissue kallikrein but not plasma kallikrein in the development of symptoms mediated by endogenous kinins in acute pancreatitis in rats
Abstract
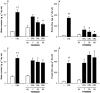
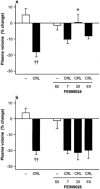
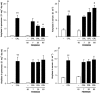
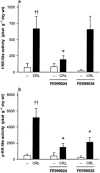
In order to investigate the mechanism of kinin release leading to vascular symptoms in acute interstitial-oedematous pancreatitis, the novel, selective inhibitors of tissue kallikrein, (2S,2'R)-2-(2'-amino-3'-(4'-chlorophenyl)propanoylamino)-N-(3-guanidinopropyl)-3-(1-naphthyl)propanoamide (FE999024, CH-2856), and of plasma kallikrein, (2'S,2"R)-4-(2'-(2"(carboxymethylamino)-3"-cyclohexyl-propanoylamino)-3'-phenyl-propanoylamino)piperidine-1-carboxamidin (FE999026, CH-4215), were used in experimental caerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. Oedema formation and plasma protein extravasation during the 2 h infusion of caerulein were inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by i.p. pretreatment with FE999024 (7-60 micromol kg(-1)) while FE999026 had no effect at the same doses. Haemoconcentration and hypovolaemia associated with the pancreatic oedema formation during pancreatitis were significantly attenuated by FE999024 at a dose of 20 micro mol kg(-1). The reduction in circulating plasma volume was not affected by FE999026. Accumulation of amylase and lipase in the pancreas was dose-dependently reduced by FE999024 while enzyme activities in the blood serum were increased by FE999024 at 60 micromol kg(-1) indicating improved enzyme removal from the tissue. Enzyme activities in the tissue and in the blood remained unaffected by FE999026. FE999024 (20 micromol kg(-1)) largely inhibited increased tissue kallikrein-like activity in the pancreas during acute pancreatitis and also strongly attenuated influx of plasma kallikrein into the tissue. FE999026 (20 micromol kg(-1)) significantly inhibited plasma kallikrein-like activity in the pancreas but had no effect on tissue kallikrein-like activity. In conclusion, vascular kinin-mediated symptoms observed during oedematous pancreatitis in the rat are caused by the action of tissue kallikrein in the pancreas whereas an involvement of plasma kallikrein seems to be unlikely.
Figures
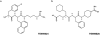
References
-
- ALLEN T.H., ORAHOVATS P.D. Spectrophotometric measurements of traces of the dye T-1824 by extraction with cellophane from blood serum and urine of normal dogs. Am. J. Physiol. 1948;154:27–38. - PubMed
-
- AMUNDSEN E., PUTTER J., FRIBERGER P., KNOS M., LARSBRATEN M., CLAESON G. Methods for the determination of glandular kallikrein by means of a chromogenic tripeptide substrate. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1979;120A:83–95. - PubMed
-
- BLOECHLE C., KÜHN R., KNOEFEL W.T., YEKEBAS E., KUSTERER K., IZBICKI J.R. Bradykinin-antagonist Hoe 140 prevents microcirculatory statis and tissue necrosis in taurocholate induced pancreatitis of the rat. Pancreas. 1994;9:783.
-
- BÜCHLER M. Objectification of the severity of acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 1991;38:101–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

