Molecular dynamics of the FixJ receiver domain: movement of the beta4-alpha4 loop correlates with the in and out flip of Phe101
- PMID: 12381845
- PMCID: PMC2373730
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0218802
Molecular dynamics of the FixJ receiver domain: movement of the beta4-alpha4 loop correlates with the in and out flip of Phe101
Abstract
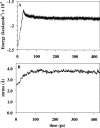
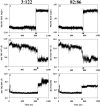
FixJ is a two-domain response regulator involved in nitrogen fixation in Sinorhizobium meliloti. Recent X-ray characterization of both the native (unphosphorylated) and the active (phosphorylated) states of the protein identify conformational changes of the beta4-alpha4 loop and the conserved residue Phe101 as the key switches in activation. These structures also allowed investigation of the transition between conformations of this two-component regulatory receiver domain by molecular dynamics simulations. The path for the conformational change was studied with a distance constraint directing the system from one state to the other. The simulations provide evidence for a correlation between the conformation of the beta4-alpha4 loop and the orientation of the residue Phe101. A model presenting the sequence of events during the activation/deactivation process is discussed.
Figures



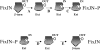
Similar articles
-
Insights into signal transduction revealed by the low resolution structure of the FixJ response regulator.J Mol Biol. 2002 Aug 16;321(3):447-57. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00651-4. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12162958
-
Conformational changes induced by phosphorylation of the FixJ receiver domain.Structure. 1999 Dec 15;7(12):1505-15. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)88341-0. Structure. 1999. PMID: 10647181
-
Phosphorylation of the Rhizobium meliloti FixJ protein induces its binding to a compound regulatory region at the fixK promoter.J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23784-9. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 8089150
-
Genetic regulation of nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium meliloti.Microbiologia. 1994 Dec;10(4):371-84. Microbiologia. 1994. PMID: 7772292 Review.
-
Identification of communication networks in Spo0F: a model for phosphorylation-induced conformational change and implications for activation of multiple domain bacterial response regulators.FEBS Lett. 1998 Mar 20;425(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00182-3. FEBS Lett. 1998. PMID: 9540996 Review.
Cited by
-
Production, characterization, and assessment of a stable analog of the response regulator CheY-phosphate from Thermotoga maritima.Protein Sci. 2017 Aug;26(8):1547-1554. doi: 10.1002/pro.3180. Epub 2017 May 14. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 28440031 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of allosteric signal transmission by information-theoretic analysis of protein dynamics.FASEB J. 2012 Feb;26(2):868-81. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-190868. Epub 2011 Nov 9. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22071506 Free PMC article.
-
Novel redox-sensing modules: accessory protein- and nucleic acid-mediated signaling.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Apr 1;16(7):668-77. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4290. Epub 2012 Jan 6. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22114914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thirty years of molecular dynamics simulations on posttranslational modifications of proteins.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2022 Nov 9;24(43):26371-26397. doi: 10.1039/d2cp02883b. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2022. PMID: 36285789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis of response regulator dephosphorylation by Rap phosphatases.PLoS Biol. 2011 Feb 8;9(2):e1000589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000589. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21346797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baikalov, I., Schroder, I., Kaczor-Grzeskowiak, M., Grzeskowiak, K., Gunsalus, R.P., and Dickerson, R.E. 1996. Structure of the Escherichia coli response regulator NarL. Biochemistry 35 11053–11061. - PubMed
-
- Birck, C., Mourey, L., Gouet, P., Fabry, B., Schumacher, J., Rousseau, P., Kahn, D., and Samama, J.P. 1999. Conformational changes induced by phosphorylation of the FixJ receiver domain. Struct. Fold. Des. 7 1505–1515. - PubMed
-
- Brooks, B., Bruccoleri, R.E., Olafson, B.D., States, D.J., Swaminathan, S., and Karplus, M. 1983. Charmm: A program for macromolecular energy minimization and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 4 187–217.
-
- Cho, H.S., Lee, S.Y., Yan, D., Pan, X., Parkinson, J.S., Kustu, S., Wemmer, D.E., and Pelton, J.G. 2000. NMR structure of activated CheY. J. Mol. Biol. 297 543–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

