Distance-scaled, finite ideal-gas reference state improves structure-derived potentials of mean force for structure selection and stability prediction
- PMID: 12381853
- PMCID: PMC2373736
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0217002
Distance-scaled, finite ideal-gas reference state improves structure-derived potentials of mean force for structure selection and stability prediction
Erratum in
- Protein Sci. 2003 Sep;12(9):2121
Abstract
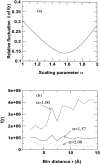
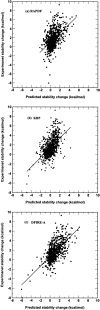
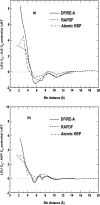
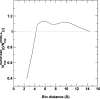
The distance-dependent structure-derived potentials developed so far all employed a reference state that can be characterized as a residue (atom)-averaged state. Here, we establish a new reference state called the distance-scaled, finite ideal-gas reference (DFIRE) state. The reference state is used to construct a residue-specific all-atom potential of mean force from a database of 1011 nonhomologous (less than 30% homology) protein structures with resolution less than 2 A. The new all-atom potential recognizes more native proteins from 32 multiple decoy sets, and raises an average Z-score by 1.4 units more than two previously developed, residue-specific, all-atom knowledge-based potentials. When only backbone and C(beta) atoms are used in scoring, the performance of the DFIRE-based potential, although is worse than that of the all-atom version, is comparable to those of the previously developed potentials on the all-atom level. In addition, the DFIRE-based all-atom potential provides the most accurate prediction of the stabilities of 895 mutants among three knowledge-based all-atom potentials. Comparison with several physical-based potentials is made.
Figures

References
-
- Altuvia, Y., Schueler, O., and Margalit, H. 1995. Ranking potential binding peptides to MHC molecules by a computational threading approach. J. Mol. Biol. 249 244–250. - PubMed
-
- Avbelj, F., Moult, J., Kitson, D.H., James, M.N., and Hagler, A.T. 1990. Molecular dynamics study of the structure and dynamics of a protein molecule in a crystalline ionic environment, Streptomyces griseus protease A. Biochemistry 29 8658–8676. - PubMed
-
- Brooks, B.R., Bruccoleri, R.E., Olafson, B.D., States, D.J., Swaminathan, S., and Karplus, M. 1983. CHARMM: A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 4 187–217.
-
- Bryant, S.H. and Lawrence, C.E. 1993. An empirical energy function for threading protein sequence through the folding motif. Proteins 16 92–112. - PubMed
-
- Casari, G. and Sippl, M.J. 1992. Structure-derived hydrophobic potential. Hydrophobic potential derived from x-ray structures of globular proteins is able to identify native folds. J. Mol. Biol. 224 725–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

