Melanization of Cryptococcus neoformans and Histoplasma capsulatum reduces their susceptibilities to amphotericin B and caspofungin
- PMID: 12384341
- PMCID: PMC128748
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.11.3394-3400.2002
Melanization of Cryptococcus neoformans and Histoplasma capsulatum reduces their susceptibilities to amphotericin B and caspofungin
Abstract
The fungal pathogens Cryptococcus neoformans and Histoplasma capsulatum produce melanin-like pigments in the presence of L-dopa in vitro and during mammalian infection. We investigated whether melanization affected the susceptibilities of the fungi to amphotericin B, caspofungin, fluconazole, itraconazole, or flucytosine (5FC). Using the standard macrodilution MIC protocol (the M27A protocol) of the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards for yeast, we found no difference in the susceptibilities of melanized and nonmelanized C. neoformans and H. capsulatum isolates. Killing assays demonstrated that melanization reduced the susceptibilities of both fungi to amphotericin B and caspofungin. Laccase-deficient C. neoformans cells grown with L-dopa were significantly more susceptible than congenic melanin-producing yeast to killing by amphotericin B or caspofungin. Preincubation of amphotericin B or caspofungin with melanins decreased their antifungal activities. Elemental analysis of melanins incubated with amphotericin B or caspofungin revealed an alteration in the C:N ratios of the melanins, which indicated binding of these drugs by the melanins. In contrast, incubation of fluconazole, itraconazole, or 5FC with melanins did not significantly affect the antifungal efficacies of the drugs or the chemical composition of the melanins. The results suggest a potential explanation for the inefficacy of caspofungin against C. neoformans in vivo, despite activity in vitro. Furthermore, the results indicate that fungal melanins protect C. neoformans and H. capsulatum from the activities of amphotericin B and caspofungin and that this protection is not demonstrable by standard broth macrodilution assays.
Figures
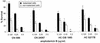
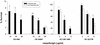
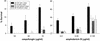

References
-
- Abruzzo, G. K., A. M. Flattery, C. J. Gill, L. Kong, J. G. Smith, V. B. Pikounis, J. M. Balkovec, A. F. Bouffard, J. F. Dropinski, H. Rosen, H. Kropp, and K. Bartizal. 1997. Evaluation of the echinocandin antifungal MK-0991 (L-743,872): efficacies in mouse models of disseminated aspergillosis, candidiasis, and cryptococcosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:2333-2338. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avramidis, N., A. Kourounakis, L. Hadjipetrou, and V. Senchuk. 1998. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating properties of grape melanin. Inhibitory effects on paw edema and adjuvant induced disease. Arzneimittelforschung 48:764-771. - PubMed
-
- Bouffard, F. A., R. A. Zambias, J. F. Dropinski, J. M. Balkovec, M. L. Hammond, G. K. Abruzzo, K. F. Bartizal, J. A. Marrinan, M. B. Kurtz, D. C. McFadden, et al. 1994. Synthesis and antifungal activity of novel cationic pneumocandin B(o) derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 37:222-225. - PubMed
-
- Casadevall, A., A. L. Rosas, and J. D. Nosanchuk. 2000. Melanin and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 3:354-358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

