L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells and ET-1 biosynthesis
- PMID: 12388093
- PMCID: PMC2924154
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00071.2002
L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells and ET-1 biosynthesis
Abstract
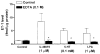
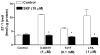
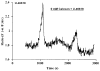
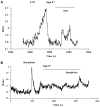
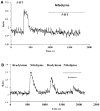
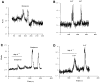
We investigated the role of intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) in endothelin-1 (ET-1) production, the effects of potential vasospastic agents on [Ca2+]i, and the presence of L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Primary cultures of endothelial cells isolated from piglet cerebral microvessels were used. Confluent cells were exposed to either the thromboxane receptor agonist U-46619 (1 microM), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT; 0.1 mM), or lysophosphatidic acid (LPA; 1 microM) alone or after pretreatment with the Ca2+-chelating agent EDTA (100 mM), the L-type Ca2+ channel blocker verapamil (10 microM), or the antagonist of receptor-operated Ca2+ channel SKF-96365 HCl (10 microM) for 15 min. ET-1 production increased from 1.2 (control) to 8.2 (U-46619), 4.9 (5-HT), or 3.9 (LPA) fmol/microg protein, respectively. Such elevated ET-1 biosynthesis was attenuated by verapamil, EDTA, or SKF-96365 HCl. To investigate the presence of L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in endothelial cells, the [Ca2+]i signal was determined fluorometrically by using fura 2-AM. Superfusion of confluent endothelial cells with U-46619, 5-HT, or LPA significantly increased [Ca2+]i. Pretreatment of endothelial cells with high K+ (60 mM) or nifedipine (4 microM) diminished increases in [Ca2+]i induced by the vasoactive agents. These results indicate that 1) elevated [Ca2+]i signals are involved in ET-1 biosynthesis induced by specific spasmogenic agents, 2) the increases in [Ca2+]i induced by the vasoactive agents tested involve receptor as well as L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels, and 3) primary cultures of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells express L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels.
Figures
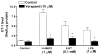

Similar articles
-
Regulation of ET-1 biosynthesis in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells by vasoactive agents and PKC.Am J Physiol. 1999 Feb;276(2):C300-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1999.276.2.C300. Am J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 9950756
-
Differential Ca2+ signaling by thrombin and protease-activated receptor-1-activating peptide in human brain microvascular endothelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Jan;286(1):C31-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00157.2003. Epub 2003 Aug 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 12944324
-
Mechanisms involved in the effects of endothelin-1 in pig prostatic small arteries.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Aug 25;640(1-3):190-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.04.059. Epub 2010 May 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20493185
-
Effects of erythropoietin on endothelin-1 synthesis and the cellular calcium messenger system in vascular endothelial cells.Am J Hypertens. 1997 Mar;10(3):289-96. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(96)00410-4. Am J Hypertens. 1997. PMID: 9056686
-
Nifedipine blocks Ca2+ store refilling through a pathway not involving L-type Ca2+ channels in rabbit arteriolar smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2001 May 1;532(Pt 3):609-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0609e.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11313433 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Calcium mobilization and Rac1 activation are required for VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1) stimulation of NADPH oxidase activity.Biochem J. 2004 Mar 1;378(Pt 2):539-47. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030794. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14594451 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of distension on airway inflammation and venular P-selectin expression.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Nov;295(5):L941-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90447.2008. Epub 2008 Sep 19. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18805956 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanosensitive cation currents through TRPC6 and Piezo1 channels in human pulmonary arterial endothelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Oct 1;323(4):C959-C973. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00313.2022. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35968892 Free PMC article.
-
Kv7 channel activation reduces brain endothelial cell permeability and prevents kainic acid-induced blood-brain barrier damage.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Mar 1;326(3):C893-C904. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00709.2023. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38284124 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 Diabetes Alters Intracellular Ca2+ Handling in Native Endothelium of Excised Rat Aorta.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 30;21(1):250. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010250. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31905880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bading H, Ginty DD, Greenberg ME. Regulation of gene expression in hippocampal neurons by distinct calcium signaling pathways. Science. 1993;260:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Berkels R, Mueller A, Roesen R, Klaus W. Nifedipine and Bay K 8644 induce an increase of [Ca2+]i and NO in endothelial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1999;4:175–181. - PubMed
-
- Bootman MD, Lipp P, Berridge MJ. The organisation and functions of local Ca2+ signals. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:2213–2222. - PubMed
-
- Bossu JL, Elhamdani A, Feltz A. Voltage-dependent calcium entry in confluent bovine capillary endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1992;299:239–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

