Rapsyn escorts the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor along the exocytic pathway via association with lipid rafts
- PMID: 12388596
- PMCID: PMC6757681
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-20-08891.2002
Rapsyn escorts the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor along the exocytic pathway via association with lipid rafts
Abstract
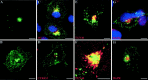
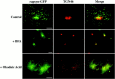
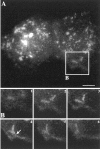
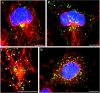
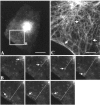
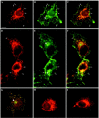
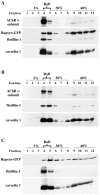
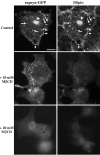
The 43 kDa receptor-associated protein rapsyn is a myristoylated peripheral protein that plays a central role in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) clustering at the neuromuscular junction. In a previous study, we demonstrated that rapsyn is specifically cotransported with AChR via post-Golgi vesicles targeted to the innervated surface of the Torpedo electrocyte (Marchand et al., 2000). In the present study, to further elucidate the mechanisms for sorting and assembly of postsynaptic proteins, we analyzed the dynamics of the intracellular trafficking of fluorescently labeled rapsyn in the transient-expressing COS-7 cell system. Our approach was based on fluorescence, time-lapse imaging, and immunoelectron microscopies, as well as biochemical analyses. We report that newly synthesized rapsyn associates with the trans-Golgi network compartment and traffics via vesiculotubular organelles toward the cell surface of COS-7 cells. The targeting of rapsyn organelles appeared to be mediated by a microtubule-dependent transport. Using cotransfection experiments of rapsyn and AChR, we observed that these two molecules codistribute within distal exocytic routes and at the plasma membrane. Triton X-100 extraction on ice and flotation gradient centrifugation demonstrated that rapsyn and AChR are recovered in low-density fractions enriched in two rafts markers: caveolin-1 and flotillin-1. We propose that sorting and targeting of these two companion molecules are mediated by association with cholesterol-sphingolipid-enriched raft microdomains. Collectively, these data highlight rapsyn as an itinerant vesicular protein that may play a dynamic role in the sorting and targeting of its companion receptor to the postsynaptic membrane. These data also raise the interesting hypothesis of the participation of the raft machinery in the targeting of signaling molecules to synaptic sites.
Figures

References
-
- Arni S, Keilbaugh SA, Ostermeyer AG, Brown DA. Association of GAP-43 with detergent-resistant membranes requires two palmitoylated cysteine residues. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28478–28485. - PubMed
-
- Banting G, Ponnambalam S. TGN38 and its orthologues: roles in post-TGN vesicle formation and maintenance of TGN morphology. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1355:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Barrantes FJ. The acetylcholine receptor ligand-gated channel as a molecular target of disease and therapeutic agents. Neurochem Res. 1997;22:391–400. - PubMed
-
- Bignami F, Camus G, Marchand S, Bailly L, Stetzkowski-Marden F, Cartaud J. Targeting of acetylcholine receptor and 43 kDa rapsyn to the postsynaptic membrane in Torpedo marmorata electrocyte. J Physiol (Paris) 1998;92:177–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
