Self-administration of intravenous buprenorphine and the buprenorphine/naloxone combination by recently detoxified heroin abusers
- PMID: 12388653
- PMCID: PMC4079473
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.102.038141
Self-administration of intravenous buprenorphine and the buprenorphine/naloxone combination by recently detoxified heroin abusers
Abstract
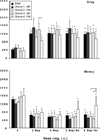
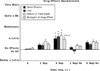
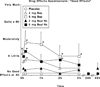
Buprenorphine is a partial mu-opioid agonist and kappa-opioid antagonist currently under development as a maintenance medication for heroin dependence. Because of concerns about illicit diversion of buprenorphine, a combination tablet containing buprenorphine and naloxone has been developed. The present study evaluated the reinforcing effects of intravenously administered placebo, buprenorphine alone (BUP; 2 and 8 mg), and the buprenorphine/naloxone combination (BUP/NX; 2 mg of buprenorphine plus 0.5 mg of naloxone, and 8 mg of buprenorphine plus 2 mg of naloxone) in recently detoxified heroin abusers during a 6-week inpatient study. Participants (n = 6) were detoxified from heroin over approximately 1 week immediately after admission. During the next 5 weeks, the reinforcing effects of placebo, BUP, and BUP/NX were evaluated. Participants first received a dose of drug and $20 and then were given the opportunity to self-administer either the dose or $20 during choice sessions. Progressive ratio break point values were significantly higher after active drug, compared with placebo, but they did not significantly differ as a function of dose or drug. In contrast, positive subjective ratings were higher after administration of BUP compared with BUP/NX, and these ratings increased in a dose-dependent manner. BUP and the combination had few effects on performance. Relative to placebo, both BUP and BUP/NX decreased pupil diameter, but there were no significant differences in pupil diameter as a function of drug or dose. These results demonstrate that both BUP and BUP/NX served as reinforcers under these conditions and that they may have similar abuse liability in recently detoxified individuals who abuse heroin.
Figures


References
-
- Amass L, Kamien JB, Reiber C, Branstetter SA. Abuse liability of IV buprenorphine-naloxone, buprenorphine, and hydromorphone in buprenorphine-naloxone maintained volunteers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2000;60(Suppl. 1):S6–S7.
-
- Baumevieille M, Haramburu F, Begaud B. Abuse of prescription medicines in southwestern France. Ann Pharmacother. 1997;31:847–850. - PubMed
-
- Bickel WK, Amass L. Buprenorphine treatment of opioid dependence: A review. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;3(4):477–489.
-
- Bigelow GE, Preston KL, Liebson IA. Abuse liability assessment of buprenorphine-naloxone combinations. In: Harris LS, editor. Problems of Drug Dependence 1986 Proceeding of the 48th Annual Scientific Meeting (National Institute on Drug Abuse Research Monograph, No. 76. Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office; 1987. pp. 145–149. - PubMed
-
- Comer SD, Collins ED, Fischman MW. Choice between money and intranasal heroin in morphine-maintained humans. Behav Pharmacol. 1997;8:677–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

