A transactivator function of cottontail rabbit papillomavirus e2 is essential for tumor induction in rabbits
- PMID: 12388680
- PMCID: PMC136747
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11209-11215.2002
A transactivator function of cottontail rabbit papillomavirus e2 is essential for tumor induction in rabbits
Abstract
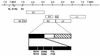
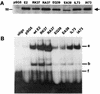
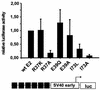
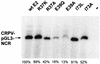
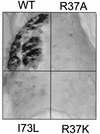
Infection of domestic rabbits with cottontail rabbit papillomavirus (CRPV) causes local papillomas which progress to carcinomas in more than 80% of cases. This animal model system therefore allows the identification of molecular mechanisms required for the induction and progression of epithelial tumors. The viral E2 protein stimulates both viral DNA replication and transcription, and these functions can be genetically separated. We introduced the respective mutations into CRPV E2 and found, in line with published data for other papillomavirus E2 proteins, that mutation of the highly conserved amino acid 37 or 73 resulted in replication-competent but transactivation-deficient E2 proteins, whereas E2 proteins with mutations at residue 39 were replication deficient and transactivation competent. The R37A, I73L, and I73A E2 mutants, showing a loss of transactivation function, and the R37K E2 mutant, which is still transactivation competent, were introduced into the whole genome of CRPV, which was then injected into the skin of rabbits. Strikingly, the ability to induce tumors within 6 weeks was abolished by each of the E2 mutations, in contrast to the tumor induction rate (93%) obtained with wild-type CRPV DNA. Two small papillomas induced by mutant E2 I73A CRPV DNA appeared as late as 12 or 24 weeks postinjection, were significantly smaller, and showed no further extension of growth. These data suggest that functionally conserved amino acids in the transactivation domain of E2 are also required for the induction and growth of epithelial tumors in rabbits infected with CRPV.
Figures
References
-
- Androphy, E. J., D. R. Lowy, and J. T. Schiller. 1987. Bovine papillomavirus E2 trans-activating gene product binds to specific sites in papillomavirus DNA. Nature (London) 325:70-73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

