Interleukin-8 and growth-regulated oncogene alpha mediate angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma
- PMID: 12388718
- PMCID: PMC136744
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11570-11583.2002
Interleukin-8 and growth-regulated oncogene alpha mediate angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma
Abstract
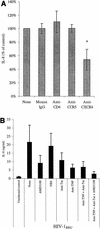
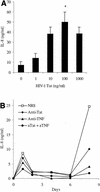
The development of the complex neoplasm Kaposi's sarcoma is dependent on infection with the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) and appears to be greatly enhanced by cytokines and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Tat. Interleukin-8 (IL-8) and growth-regulated oncogene alpha (GRO-alpha) are chemokines involved in chemoattraction, neovascularization, and stimulation of HIV-1 replication. We have previously demonstrated that production of GRO-alpha is stimulated by exposure of monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) to HIV-1. Here we show that exposure of MDM to HIV-1, viral Tat, or viral gp120 leads to a substantial increase in IL-8 production. We also demonstrate that IL-8 and GRO-alpha are induced by KSHV infection of endothelial cells and are crucial to the angiogenic phenotype developed by KSHV-infected endothelial cells in cell culture and upon implantation into SCID mice. Thus, the three known etiological factors in Kaposi's sarcoma pathogenesis-KSHV, HIV-1 Tat, and cellular growth factors-might be linked, in part, through induction of IL-8 and GRO-alpha.
Figures





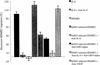



Similar articles
-
Chemokines activate Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus G protein-coupled receptor in mammalian cells in culture.J Clin Invest. 1998 Oct 15;102(8):1469-72. doi: 10.1172/JCI4461. J Clin Invest. 1998. PMID: 9788958 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Tat of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activates lytic cycle replication of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: role of JAK/STAT signaling.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(5):2401-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02024-06. Epub 2006 Dec 6. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17151125 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-induced GRO-alpha production stimulates HIV-1 replication in macrophages and T lymphocytes.J Virol. 2001 Jul;75(13):5812-22. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.13.5812-5822.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11390582 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma pathogenesis: a link between immunology and tumor biology.Crit Rev Oncog. 1998;9(2):107-24. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v9.i2.20. Crit Rev Oncog. 1998. PMID: 9973245 Review.
-
Angiogenic effects of extracellular human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein and its role in the pathogenesis of AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002 Apr;15(2):310-26. doi: 10.1128/CMR.15.2.310-326.2002. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002. PMID: 11932235 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sulfotyrosines of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus G protein-coupled receptor promote tumorigenesis through autocrine activation.J Virol. 2010 Apr;84(7):3351-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01939-09. Epub 2010 Jan 27. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20106924 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the complexities of SARS-CoV2 infection and its immunology: A road to immune-based therapeutics.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Nov;88:106980. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106980. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33182073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces rapid release of angiopoietin-2 from endothelial cells.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(11):6326-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03303-12. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23536671 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus K15 protein contributes to virus-induced angiogenesis by recruiting PLCγ1 and activating NFAT1-dependent RCAN1 expression.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002927. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002927. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23028325 Free PMC article.
-
Tumorigenesis by human herpesvirus 8 vGPCR is accelerated by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(17):9336-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.17.9336-9342.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15308728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkhatib, G., C. Combadiere, C. C. Broder, Y. Feng, P. E. Kennedy, P. M. Murphy, and E. A. Berger. 1996. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science 272:1955-1958. - PubMed
-
- Ariyoshi, K., M. Schim van der Loeff, P. Cook, D. Whitby, T. Corrah, S. Jaffar, F. Cham, S. Sabally, D. O'Donovan, R. A. Weiss, T. F. Schulz, and H. Whittle. 1998. Kaposi's sarcoma in the Gambia, West Africa, is less frequent in human immunodeficiency virus type 2 than in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection despite a high prevalence of human herpesvirus 8. J. Hum. Virol. 1:193-199. - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini, M., B. Dewald, and B. Moser. 1994. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines—CXC and CC chemokines. Adv. Immunol. 55:97-179. - PubMed
-
- Barillari, G., R. Gendelman, R. C. Gallo, and B. Ensoli. 1993. The Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, a growth factor for AIDS Kaposi sarcoma and cytokine-activated vascular cells, induces adhesion of the same cell types by using integrin receptors recognizing the RGD amino acid sequence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:7941-7945. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beral, V., T. A. Peterman, R. L. Berkelman, and H. W. Jaffe. 1990. Kaposi's sarcoma among persons with AIDS: a sexually transmitted infection? Lancet 335:123-128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DE13161/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007528/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL063614/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI36685/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA64416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL63614/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL39926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM07315/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM07863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI 07528/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL57885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007315/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

