Escape in one of two cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes bound by a high-frequency major histocompatibility complex class I molecule, Mamu-A*02: a paradigm for virus evolution and persistence?
- PMID: 12388723
- PMCID: PMC136802
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11623-11636.2002
Escape in one of two cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes bound by a high-frequency major histocompatibility complex class I molecule, Mamu-A*02: a paradigm for virus evolution and persistence?
Abstract
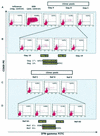
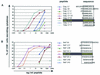
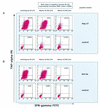
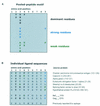
It is now accepted that an effective vaccine against AIDS must include effective cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte (CTL) responses. The simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-infected rhesus macaque is the best available animal model for AIDS, but analysis of macaque CTL responses has hitherto focused mainly on epitopes bound by a single major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule, Mamu-A*01. The availability of Mamu-A*01-positive macaques for vaccine studies is therefore severely limited. Furthermore, it is becoming clear that different CTL responses are able to control immunodeficiency virus replication with varying success, making it a priority to identify and analyze CTL responses restricted by common MHC class I molecules other than Mamu-A*01. Here we describe two novel epitopes derived from SIV, one from Gag (Gag(71-79) GY9), and one from the Nef protein (Nef(159-167) YY9). Both epitopes are bound by the common macaque MHC class I molecule, Mamu-A*02. The sequences of these two eptiopes are consistent with the molecule's peptide-binding motif, which we have defined by elution of natural ligands from Mamu-A*02. Strikingly, we found evidence for the selection of escape variant viruses by CTL specific for Nef(159-167) YY9 in 6 of 6 Mamu-A*02-positive animals. In contrast, viral sequences encoding the Gag(71-79) GY9 epitope remained intact in each animal. This situation is reminiscent of Mamu-A*01-restricted CTL that recognize Tat(28-35) SL8, which reproducibly selects for escape variants during acute infection, and Gag(181-189) CM9, which does not. Differential selection by CTL may therefore be a paradigm of immunodeficiency virus infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Definition of five new simian immunodeficiency virus cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes and their restricting major histocompatibility complex class I molecules: evidence for an influence on disease progression.J Virol. 2000 Aug;74(16):7400-10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.16.7400-7410.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10906193 Free PMC article.
-
Dominance of CD8 responses specific for epitopes bound by a single major histocompatibility complex class I molecule during the acute phase of viral infection.J Virol. 2002 Jan;76(2):875-84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.2.875-884.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11752176 Free PMC article.
-
CD8(+) lymphocytes from simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques recognize 14 different epitopes bound by the major histocompatibility complex class I molecule mamu-A*01: implications for vaccine design and testing.J Virol. 2001 Jan;75(2):738-49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.2.738-749.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11134287 Free PMC article.
-
Simian immunodeficiency virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in rhesus monkeys: characterization and vaccine induction.Semin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):215-23. doi: 10.1006/smim.1993.1025. Semin Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8394161 Review.
-
Understanding cytotoxic T-lymphocyte escape during simian immunodeficiency virus infection.Immunol Rev. 2001 Oct;183:115-26. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1830110.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11782252 Review.
Cited by
-
Unparalleled complexity of the MHC class I region in rhesus macaques.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 1;102(5):1626-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409084102. Epub 2005 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15665097 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of antiretroviral therapy 48 hours after infection with simian immunodeficiency virus potently suppresses acute-phase viremia and blocks the massive loss of memory CD4+ T cells but fails to prevent disease.J Virol. 2009 Jul;83(14):7099-108. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02522-08. Epub 2009 May 6. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19420078 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory TCR coreceptor PD-1 is a sensitive indicator of low-level replication of SIV and HIV-1.J Immunol. 2010 Jan 1;184(1):476-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902781. Epub 2009 Nov 30. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19949078 Free PMC article.
-
Selective depletion of high-avidity human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-specific CD8+ T cells after early HIV-1 infection.J Virol. 2007 Apr;81(8):4199-214. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01388-06. Epub 2007 Feb 7. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17287271 Free PMC article.
-
Not all cytokine-producing CD8+ T cells suppress simian immunodeficiency virus replication.J Virol. 2007 Feb;81(3):1517-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01780-06. Epub 2006 Nov 29. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17135324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, T. M., B. R. Mothe, J. Sidney, P. Jing, J. L. Dzuris, M. E. Liebl, T. U. Vogel, D. H. O'Connor, X. Wang, M. C. Wussow, J. A. Thomson, J. D. Altman, D. I. Watkins, and A. Sette. 2001. CD8+ lymphocytes from simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques recognize 14 different epitopes bound by the major histocompatibility complex class I molecule Mamu-A*01: implications for vaccine design and testing. J. Virol. 75:738-749. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen, T. M., D. H. O'Connor, P. Jing, J. L. Dzuris, B. R. Mothe, T. U. Vogel, E. Dunphy, M. E. Liebl, C. Emerson, N. Wilson, K. J. Kunstman, X. Wang, D. B. Allison, A. L. Hughes, R. C. Desrosiers, J. D. Altman, S. M. Wolinsky, A. Sette, and D. I. Watkins. 2000. Tat-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes select for SIV escape variants during resolution of primary viraemia. Nature 407:386-390. - PubMed
-
- Allen, T. M., J. Sidney, M. F. del Guercio, R. L. Glickman, G. L. Lensmeyer, D. A. Wiebe, R. DeMars, C. D. Pauza, R. P. Johnson, A. Sette, and D. I. Watkins. 1998. Characterization of the peptide binding motif of a rhesus MHC class I molecule (Mamu-A*01) that binds an immunodominant CTL epitope from simian immunodeficiency virus. J. Immunol. 160:6062-6071. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, M. G., D. Hauer, D. P. Sharma, S. V. Joag, O. Narayan, M. C. Zink, and J. E. Clements. 1993. Analysis of envelope changes acquired by SIVmac239 during neuroadaption in rhesus macaques. Virology 195:616-626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

