Distribution and evolution of von Willebrand/integrin A domains: widely dispersed domains with roles in cell adhesion and elsewhere
- PMID: 12388743
- PMCID: PMC129952
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-05-0259
Distribution and evolution of von Willebrand/integrin A domains: widely dispersed domains with roles in cell adhesion and elsewhere
Abstract
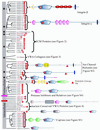
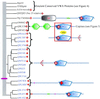
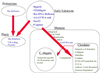
The von Willebrand A (VWA) domain is a well-studied domain involved in cell adhesion, in extracellular matrix proteins, and in integrin receptors. A number of human diseases arise from mutations in VWA domains. We have analyzed the phylogenetic distribution of this domain and the relationships among approximately 500 proteins containing this domain. Although the majority of VWA-containing proteins are extracellular, the most ancient ones, present in all eukaryotes, are all intracellular proteins involved in functions such as transcription, DNA repair, ribosomal and membrane transport, and the proteasome. A common feature seems to be involvement in multiprotein complexes. Subsequent evolution involved deployment of VWA domains by Metazoa in extracellular proteins involved in cell adhesion such as integrin beta subunits (all Metazoa). Nematodes and chordates separately expanded their complements of extracellular matrix proteins containing VWA domains, whereas plants expanded their intracellular complement. Chordates developed VWA-containing integrin alpha subunits, collagens, and other extracellular matrix proteins (e.g., matrilins, cochlin/vitrin, and von Willebrand factor). Consideration of the known properties of VWA domains in integrins and extracellular matrix proteins allows insights into their involvement in protein-protein interactions and the roles of bound divalent cations and conformational changes. These allow inferences about similar functions in novel situations such as protease regulators (e.g., complement factors and trypsin inhibitors) and intracellular proteins (e.g., helicases, chelatases, and copines).
Figures




References
-
- Adams MD, et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- Anand G, Yin X, Shahidi AK, Grove L, Prochownik EV. Novel regulation of the helix-loop-helix protein Id1 by S5a, a subunit of the 26 S proteasome. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19140–19151. - PubMed
-
- Anantharaman V, Aravind L. Cachea signaling domain common to animal Ca(2+)-channel subunits, and a class of prokaryotic chemotaxis receptors. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:535–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

