A novel conserved RNA-binding domain protein, RBD-1, is essential for ribosome biogenesis
- PMID: 12388766
- PMCID: PMC129975
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-03-0138
A novel conserved RNA-binding domain protein, RBD-1, is essential for ribosome biogenesis
Abstract
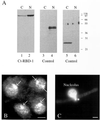
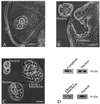
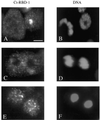
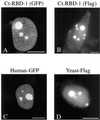
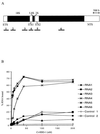
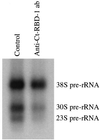
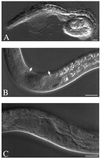
Synthesis of the ribosomal subunits from pre-rRNA requires a large number of trans-acting proteins and small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein particles to execute base modifications, RNA cleavages, and structural rearrangements. We have characterized a novel protein, RNA-binding domain-1 (RBD-1), that is involved in ribosome biogenesis. This protein contains six consensus RNA-binding domains and is conserved as to sequence, domain organization, and cellular location from yeast to human. RBD-1 is essential in Caenorhabditis elegans. In the dipteran Chironomus tentans, RBD-1 (Ct-RBD-1) binds pre-rRNA in vitro and anti-Ct-RBD-1 antibodies repress pre-rRNA processing in vivo. Ct-RBD-1 is mainly located in the nucleolus in an RNA polymerase I transcription-dependent manner, but it is also present in discrete foci in the interchromatin and in the cytoplasm. In cytoplasmic extracts, 20-30% of Ct-RBD-1 is associated with ribosomes and, preferentially, with the 40S ribosomal subunit. Our data suggest that RBD-1 plays a role in structurally coordinating pre-rRNA during ribosome biogenesis and that this function is conserved in all eukaryotes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RBD-1, a nucleolar RNA-binding protein, is essential for Caenorhabditis elegans early development through 18S ribosomal RNA processing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Feb 10;32(3):1028-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh264. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14872060 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of human Nop56p-associated pre-ribosomal ribonucleoprotein complexes. Possible link between Nop56p and the nucleolar protein treacle responsible for Treacher Collins syndrome.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 5;278(36):34309-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304304200. Epub 2003 May 30. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12777385
-
Bop1 is a mouse WD40 repeat nucleolar protein involved in 28S and 5. 8S RRNA processing and 60S ribosome biogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;20(15):5516-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.15.5516-5528.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10891491 Free PMC article.
-
A new layer of rRNA regulation by small interference RNAs and the nuclear RNAi pathway.RNA Biol. 2017 Nov 2;14(11):1492-1498. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1341034. Epub 2017 Jul 21. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28640690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins in ribosome synthesis.Mol Biol Rep. 1990;14(2-3):103-6. doi: 10.1007/BF00360433. Mol Biol Rep. 1990. PMID: 2141891 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
RBD-1, a nucleolar RNA-binding protein, is essential for Caenorhabditis elegans early development through 18S ribosomal RNA processing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Feb 10;32(3):1028-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh264. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14872060 Free PMC article.
-
Chironomus tentans-repressor splicing factor represses SR protein function locally on pre-mRNA exons and is displaced at correct splice sites.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Jan;17(1):32-42. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-04-0339. Epub 2005 Oct 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16236800 Free PMC article.
-
RBM19 is essential for preimplantation development in the mouse.BMC Dev Biol. 2008 Dec 16;8:115. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-8-115. BMC Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 19087264 Free PMC article.
-
Mrd1p binds to pre-rRNA early during transcription independent of U3 snoRNA and is required for compaction of the pre-rRNA into small subunit processomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Aug;36(13):4364-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn384. Epub 2008 Jun 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18586827 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary conservation of the ribosomal biogenesis factor Rbm19/Mrd1: implications for function.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e43786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043786. Epub 2012 Sep 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allain FH-T, Gubser CC, Howe PWA, Nagai K, Neuhaus D, Varani G. Specificity of ribonucleoprotein interaction determined by RNA folding during complex formation. Nature. 1996;380:646–650. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AKL, Lam YW, Steen H, Mann M, Lamond AI. Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Biamonti G, Riva S. New insights into the auxiliary domains of eukaryotic RNA binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1994;340:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

