Resolvins: a family of bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits initiated by aspirin treatment that counter proinflammation signals
- PMID: 12391014
- PMCID: PMC2194036
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20020760
Resolvins: a family of bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits initiated by aspirin treatment that counter proinflammation signals
Abstract
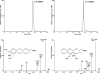
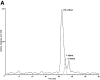
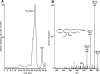
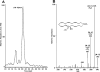
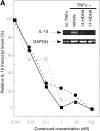
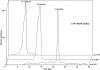
Aspirin (ASA) is unique among current therapies because it acetylates cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 enabling the biosynthesis of R-containing precursors of endogenous antiinflammatory mediators. Here, we report that lipidomic analysis of exudates obtained in the resolution phase from mice treated with ASA and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (C22:6) produce a novel family of bioactive 17R-hydroxy-containing di- and tri-hydroxy-docosanoids termed resolvins. Murine brain treated with aspirin produced endogenous 17R-hydroxydocosahexaenoic acid as did human microglial cells. Human COX-2 converted DHA to 13-hydroxy-DHA that switched with ASA to 17R-HDHA that also proved a major route in hypoxic endothelial cells. Human neutrophils transformed COX-2-ASA-derived 17R-hydroxy-DHA into two sets of novel di- and trihydroxy products; one initiated via oxygenation at carbon 7 and the other at carbon 4. These compounds inhibited (IC(50) approximately 50 pM) microglial cell cytokine expression and in vivo dermal inflammation and peritonitis at ng doses, reducing 40-80% leukocytic exudates. These results indicate that exudates, vascular, leukocytes and neural cells treated with aspirin convert DHA to novel 17R-hydroxy series of docosanoids that are potent regulators. These biosynthetic pathways utilize omega-3 DHA and EPA during multicellular events in resolution to produce a family of protective compounds, i.e., resolvins, that enhance proresolution status.
Figures








References
-
- Serhan, C.N., C.B. Clish, J. Brannon, S.P. Colgan, N. Chiang, and K. Gronert. 2000. Novel functional sets of lipid-derived mediators with antiinflammatory actions generated from omega-3 fatty acids via cyclooxygenase 2-nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and transcellular processing. J. Exp. Med. 192:1197–1204. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Samuelsson, B. 1982. From studies of biochemical mechanisms to novel biological mediators: prostaglandin endoperoxides, thromboxanes and leukotrienes. Les Prix Nobel: nobel prizes, presentations, biographies and lectures. Almqvist & Wiksell, Stockholm. 153–174.
-
- Samuelsson, B., S.E. Dahlén, J.Å. Lindgren, C.A. Rouzer, and C.N. Serhan. 1987. Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science. 237:1171–1176. - PubMed
-
- Gunstone, F.D., J.L. Harwood, and F.B. Padley, editors. 1994. The Lipid Handbook. 2nd ed. Chapman & Hall, London. pp. 1–1273.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

