KaiA-stimulated KaiC phosphorylation in circadian timing loops in cyanobacteria
- PMID: 12391300
- PMCID: PMC137794
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.222467299
KaiA-stimulated KaiC phosphorylation in circadian timing loops in cyanobacteria
Abstract
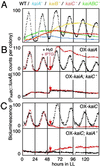
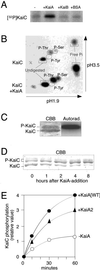
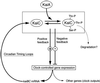
Cyanobacterial clock proteins KaiA and KaiC are proposed as positive and negative regulators in the autoregulatory circadian kaiBC expression, respectively. Here, we show that activation of kaiBC expression by kaiA requires KaiC, suggesting a positive feedback control in the cyanobacterial clockwork. We found that robust circadian phosphorylation of KaiC. KaiA was essential for in vivo KaiC phosphorylation and activated in vitro KaiC autophosphorylation. These effects of KaiA were attenuated by the kaiA2 long period mutation. Both the long period phenotype and the abnormal KaiC phosphorylation in this mutant were suppressed by a previously undocumented kaiC mutation. We propose that KaiA-stimulated circadian KaiC phosphorylation is important for circadian timing.
Figures


References
-
- Iwasaki H. & Kondo, T. (2000) Plant Cell Physiol. 41 1013-1020. - PubMed
-
- Mori T. & Johnson, C. H. (2001) Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 12 271-278. - PubMed
-
- Ishiura M., Kutsuna, S., Aoki, S., Iwasaki, H., Andersson, C. R., Johnson, C. H., Golden, S. S. & Kondo, T. (1998) Science 281 1519-1523. - PubMed
-
- Young M. W. & Kay, S. A. (2001) Nat. Rev. Genet. 2 702-715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

