Bidirectional plasticity of excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)-spike coupling in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons
- PMID: 12391303
- PMCID: PMC137914
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.222546399
Bidirectional plasticity of excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)-spike coupling in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons
Abstract
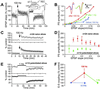
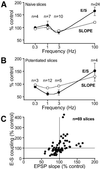
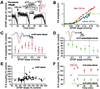
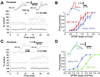
Integration of synaptic excitation to generate an action potential (excitatory postsynaptic potential-spike coupling or E-S coupling) determines the neuronal output. Bidirectional synaptic plasticity is well established in the hippocampus, but whether active synaptic integration can display potentiation and depression remains unclear. We show here that synaptic depression is associated with an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-dependent and long-lasting depression of E-S coupling. E-S depression is input-specific and is expressed in the presence of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A and B receptor antagonists. In single neurons, E-S depression is observed without modification of postsynaptic passive properties. We conclude that a decrease in intrinsic excitability underlies E-S depression and is synergic with glutamatergic long-term depression.
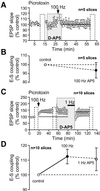
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pentobarbital enhances gamma-aminobutyric acid-mediated excitation without altering synaptic plasticity in rat hippocampus.Anesth Analg. 2007 Apr;104(4):840-6. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000256874.33810.3a. Anesth Analg. 2007. PMID: 17377091
-
Intracellular correlate of EPSP-spike potentiation in CA1 pyramidal neurons is controlled by GABAergic modulation.Hippocampus. 2003;13(7):801-5. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10129. Hippocampus. 2003. PMID: 14620875
-
Induction mechanisms and modulation of bidirectional burst stimulation-induced synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Jul;28(2):279-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06337.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18702699
-
Synergistic excitability plasticity in cerebellar functioning.FEBS J. 2020 Nov;287(21):4557-4593. doi: 10.1111/febs.15355. Epub 2020 Jun 11. FEBS J. 2020. PMID: 32367676 Review.
-
Synaptic properties of newly generated granule cells support sparse coding in the adult hippocampus.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Oct 17;372:112036. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112036. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31201871 Review.
Cited by
-
Bidirectional plasticity of intrinsic excitability controls sensory inputs efficiency in layer 5 barrel cortex neurons in vivo.J Neurosci. 2012 Aug 15;32(33):11377-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0415-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22895720 Free PMC article.
-
Timing and balance of inhibition enhance the effect of long-term potentiation on cell firing.J Neurosci. 2004 Oct 6;24(40):8873-84. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2661-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15470154 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic plasticity complements long-term potentiation in parallel fiber input gain control in cerebellar Purkinje cells.J Neurosci. 2010 Oct 13;30(41):13630-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3226-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20943904 Free PMC article.
-
A new principle for information storage in an enzymatic pathway model.PLoS Comput Biol. 2007 Jun;3(6):e124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030124. Epub 2007 May 18. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007. PMID: 17590079 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term plasticity is proportional to theta-activity.PLoS One. 2009 Jun 9;4(6):e5850. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005850. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19513114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spruston N., Jaffe, D. B. & Johnston, D. (1994) Trends Neurosci. 17, 161-166. - PubMed
-
- Magee J. F. (2000) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 1, 181-190. - PubMed
-
- Bliss T. V. P., Lømo, T. & Gardner-Medwin, A. R. (1973) in Macromolecules and Behaviour, eds. Ansell, G. & Bradley, P. B. (MacMillan, London), pp. 193–203.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

