A family of RIM-binding proteins regulated by alternative splicing: Implications for the genesis of synaptic active zones
- PMID: 12391317
- PMCID: PMC137906
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.182532999
A family of RIM-binding proteins regulated by alternative splicing: Implications for the genesis of synaptic active zones
Abstract
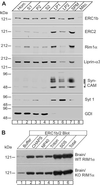
RIMs are presynaptic active zone proteins that regulate neurotransmitter release. We describe two related genes that encode proteins with identical C-terminal sequences that bind to the conserved PDZ domain of RIMs via an unusual PDZ-binding motif. These proteins were previously reported separately as ELKS, Rab6-interacting protein 2, and CAST, leading us to refer to them by the acronym ERC. Alternative splicing of the C terminus of ERC1 generates a longer ERC1a variant that does not bind to RIMs and a shorter ERC1b variant that binds to RIMs, whereas the C terminus of ERC2 is synthesized only in a single RIM-binding variant. ERC1a is expressed ubiquitously as a cytosolic protein outside of brain; ERC1b is detectable only in brain, where it is both a cytosolic protein and an insoluble active zone component; and ERC2 is brain-specific but exclusively localized to active zones. Only brain-specific ERCs bind to RIMs, but both ubiquitous and brain-specific ERCs bind to Rab6, a GTP-binding protein involved in membrane traffic at the Golgi complex. ERC1a and ERC1b/2 likely perform similar functions at distinct localizations, indicating unexpected connections between nonneuronal membrane traffic at the Golgi complex executed via Rab6 and neuronal membrane traffic at the active zone executed via RIMs.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The RIM/NIM family of neuronal C2 domain proteins. Interactions with Rab3 and a new class of Src homology 3 domain proteins.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jun 30;275(26):20033-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M909008199. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10748113
-
Interaction of the ERC family of RIM-binding proteins with the liprin-alpha family of multidomain proteins.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 24;278(43):42377-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307561200. Epub 2003 Aug 15. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12923177
-
Aczonin, a 550-kD putative scaffolding protein of presynaptic active zones, shares homology regions with Rim and Bassoon and binds profilin.J Cell Biol. 1999 Oct 4;147(1):151-62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.1.151. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10508862 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular organization and assembly of the presynaptic active zone of neurotransmitter release.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;43:49-68. doi: 10.1007/400_012. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006. PMID: 17068967 Review.
-
Molecular organization of the presynaptic active zone.Cell Tissue Res. 2006 Nov;326(2):379-91. doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0244-y. Epub 2006 Jul 25. Cell Tissue Res. 2006. PMID: 16865347 Review.
Cited by
-
A post-transcriptional regulatory switch in polypyrimidine tract-binding proteins reprograms alternative splicing in developing neurons.Genes Dev. 2007 Jul 1;21(13):1636-52. doi: 10.1101/gad.1558107. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17606642 Free PMC article.
-
ELKS, a protein structurally related to the active zone-associated protein CAST, is expressed in pancreatic beta cells and functions in insulin exocytosis: interaction of ELKS with exocytotic machinery analyzed by total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3289-300. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0816. Epub 2005 May 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15888548 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Synaptic Vesicle Exo- and Endocytosis.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 4;10(7):1593. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071593. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presynaptic Cytomatrix Proteins.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;33:23-42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-34229-5_2. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37615862
-
The active zone protein family ELKS supports Ca2+ influx at nerve terminals of inhibitory hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2014 Sep 10;34(37):12289-303. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0999-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25209271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geppert M., Bolshakov, V. Y., Siegelbaum, S. A., Takei, K., De Camilli, P., Hammer, R. E. & Südhof, T. C. (1994) Nature 369, 493-497. - PubMed
-
- Geppert M., Goda, Y., Stevens, C. F. & Südhof, T. C. (1997) Nature 387, 810-814. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Okamoto, M., Schmitz, F., Hofman, K. & Südhof, T. C. (1997) Nature 388, 593-598. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Sugita, S. & Südhof, T. C. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 20033-20044. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

